In SQL Server, the UNION operator is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements.
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
UNION
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];Parameter explanation
expression1, expression2, … expression_n: expressions specify the columns or calculations that you want to compare between the two SELECT statements.
tables: It specifies the tables that you want to retrieve records from. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause.
WHERE conditions: It is optional condition. It specifies the conditions that must be met for the records to be selected.
Image representation:
Note: The covered blue area specifies the union data.
UNION operator with single expression
Example:
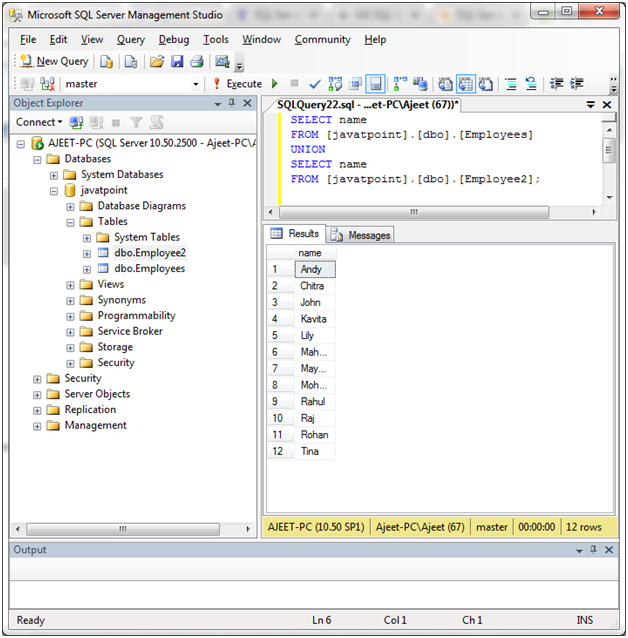
SELECT name
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
UNION
SELECT name
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employee2];Output:
UNION operator with multiple expressions
Example:
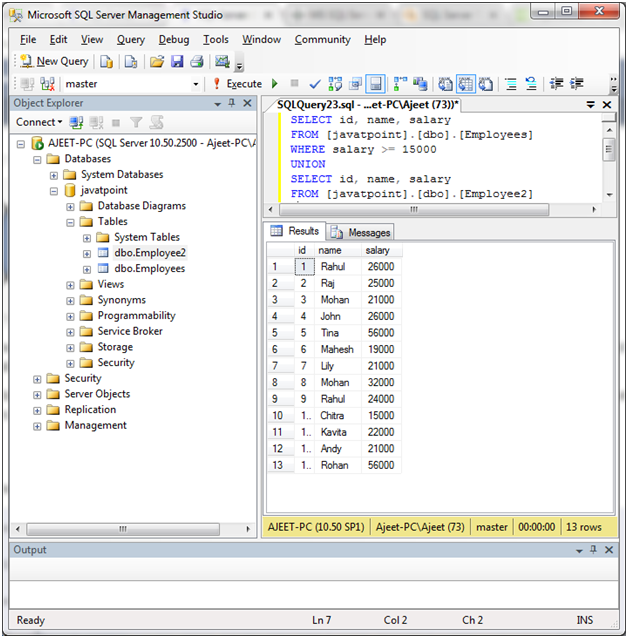
Let’s use multiple expressions of each table. For example: id, name, salary.
SELECT id, name, salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary >= 15000
UNION
SELECT id, name, salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employee2]Output:
UNION ALL Operator
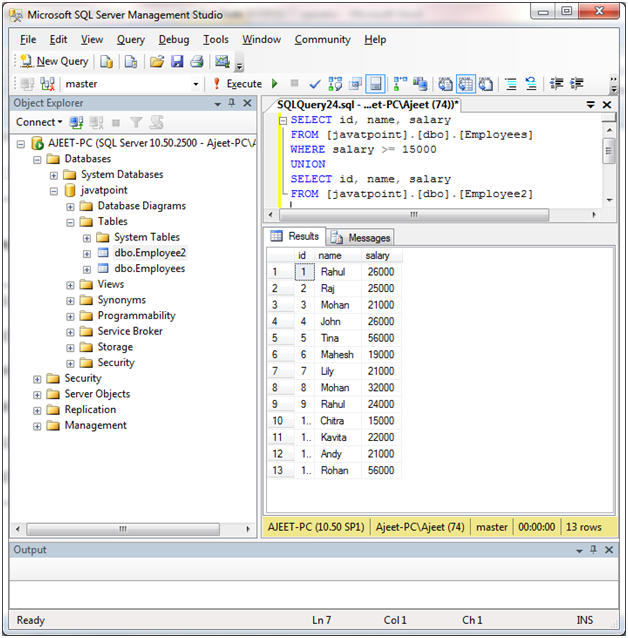
The UNION operator selects only distinct values by default. So, the UNION ALL operator is used to allow duplicate values also.
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;SELECT id, name, salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary >= 15000
UNION
SELECT id, name, salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employee2Output:
Leave a Reply