The SQL Server IS NULL operator is used to test for a NULL value.
expression IS NULL Parameter explanation
expression: It specifies a value whether it is NULL.
Note:
If the expression is NULL value then the condition evaluates to TRUE.
If expression is not a NULL value, the condition evaluates to FALSE.
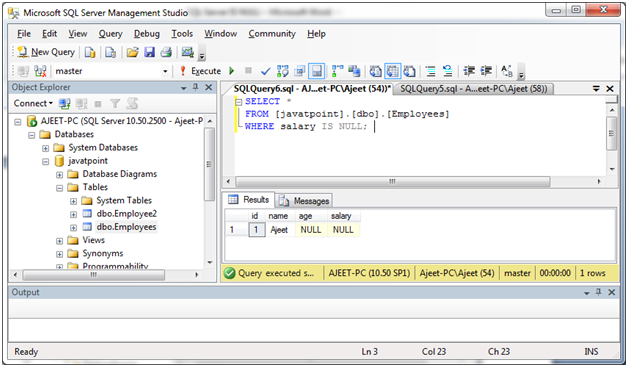
IS NULL Operator with SELECT Statement
SELECT *
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary IS NULL;Output:
IS NULL Operator with INSERT Statement
INSERT INTO [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
(id, name, salary)
SELECT id, name, Department
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employee2]
WHERE name IS NULL;Output:
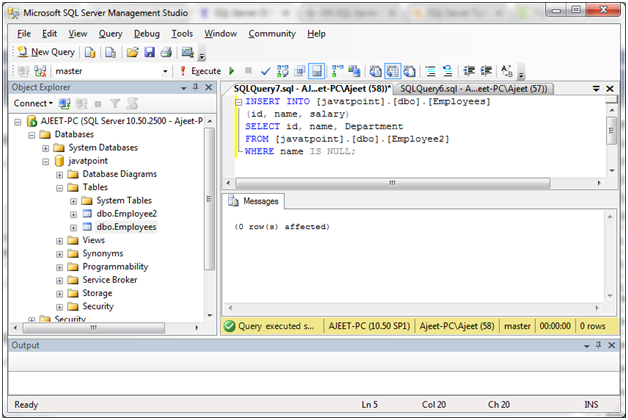
Note: This displays “0 rows affected” because there is no NULL value in name in the “Employees” table.
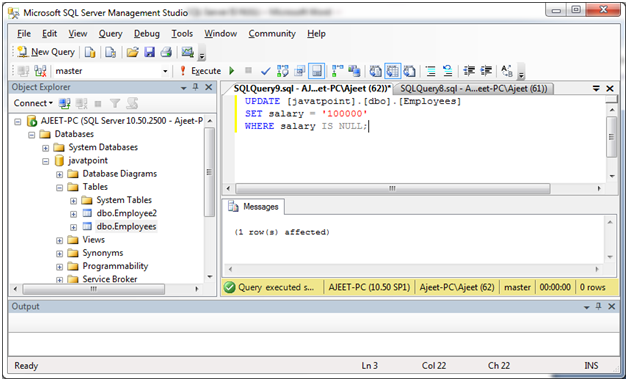
IS NULL Operator with UPDATE Statement
Example:
Update the salary of the employees in “Employees” table and set to 100000 where salary is NULL.
UPDATE Employees
SET salary = '100000'
WHERE salary IS NULL;Output:
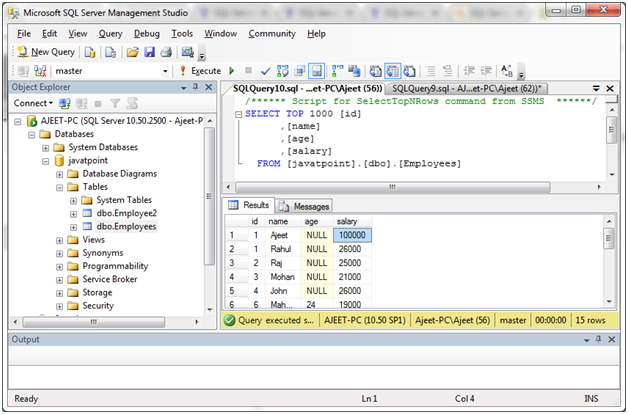
You can verify it by using SELECT query:
IS NULL Operator with DELETE Statement
Delete the employees from the “Employees” table where age is NULL.
DELETE FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE age IS NULL;Output:
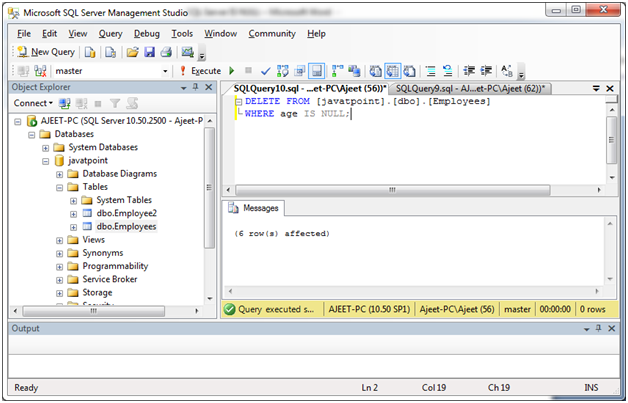
You can verify it by using SELECT query:
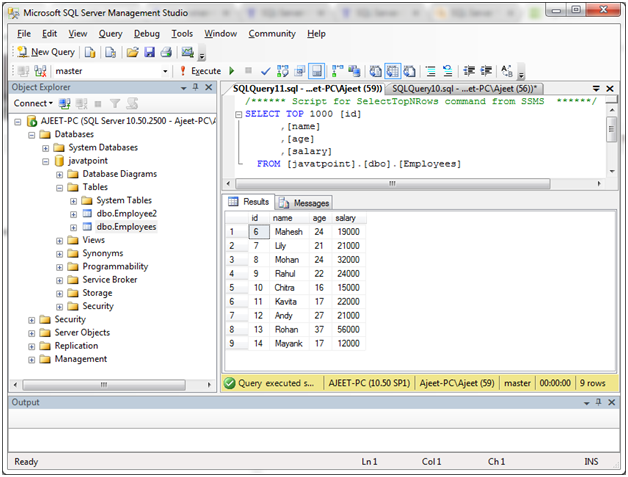
You can see that there is no NULL value in age in the above table.
Leave a Reply