ON DELETE CASCADE clause in MySQL is used to automatically remove the matching records from the child table when we delete the rows from the parent table. It is a kind of referential action related to the foreign key.
Suppose we have created two tables with a FOREIGN KEY in a foreign key relationship, making both tables a parent and child. Next, we define an ON DELETE CASCADE clause for one FOREIGN KEY that must be set for the other to succeed in the cascading operations. If the ON DELETE CASCADE is defined for one FOREIGN KEY clause only, then cascading operations will throw an error.
MySQL ON DELETE CASCADE Example
Let us understand how we can use the ON DELETE CASCADE clause in the MySQL table. First, we are going to create two tables named Employee and Payment. Both tables are related through a foreign key with on delete cascade operation. Here, an Employee is the parent table, and Payment is the child table. The following scripts create both tables along with their records.
Table: Employee
The following statement creates a table Employee:
CREATE TABLE Employee (
emp_id int(10) NOT NULL,
name varchar(40) NOT NULL,
birthdate date NOT NULL,
gender varchar(10) NOT NULL,
hire_date date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_id)
); Next, execute the insert query to fill the records.
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, name, birthdate, gender, hire_date) VALUES
(101, 'Bryan', '1988-08-12', 'M', '2015-08-26'),
(102, 'Joseph', '1978-05-12', 'M', '2014-10-21'),
(103, 'Mike', '1984-10-13', 'M', '2017-10-28'),
(104, 'Daren', '1979-04-11', 'M', '2006-11-01'),
(105, 'Marie', '1990-02-11', 'F', '2018-10-12'); Execute the SELECT query to verify the data into a table, which can be shown below:
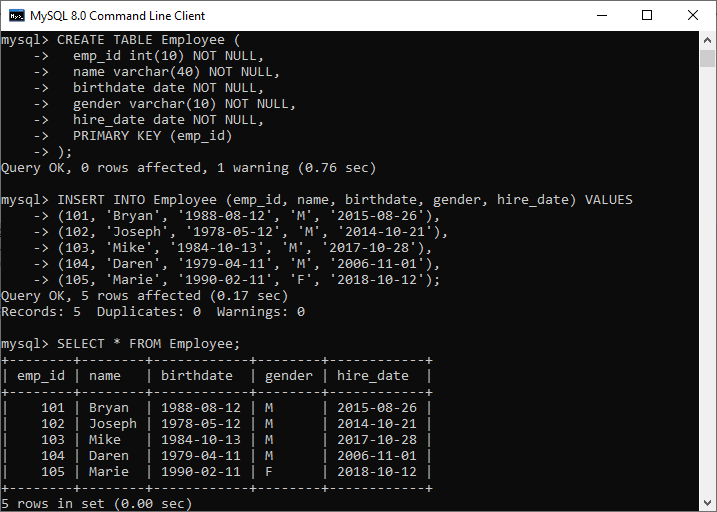
Table: Payment
The below statement creates a table Payment:
CREATE TABLE Payment (
payment_id int(10) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
emp_id int(10) NOT NULL,
amount float NOT NULL,
payment_date date NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (emp_id) REFERENCES Employee (emp_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
); Next, execute the insert statement to fill the records into a table.
INSERT INTO Payment (payment_id, emp_id, amount, payment_date) VALUES
(301, 101, 1200, '2015-09-15'),
(302, 101, 1200, '2015-09-30'),
(303, 101, 1500, '2015-10-15'),
(304, 101, 1500, '2015-10-30'),
(305, 102, 1800, '2015-09-15'),
(306, 102, 1800, '2015-09-30'); Execute the SELECT query to verify the data into a table, which can be shown below:
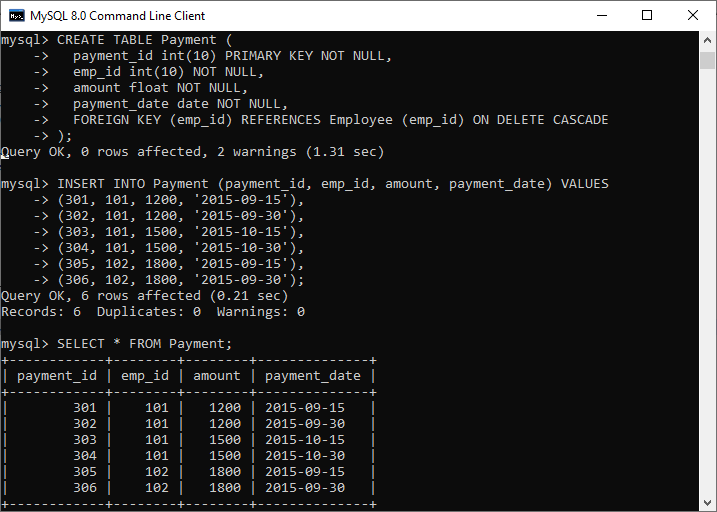
Let us delete data from the parent table Employee. To do this, execute the following statement:
mysql> DELETE FROM Employee WHERE emp_id = 102; The above statement will delete the employee records whose emp_id = 102 and referencing data into the child table. We can verify the data using the SELECT statement that will give the following output:
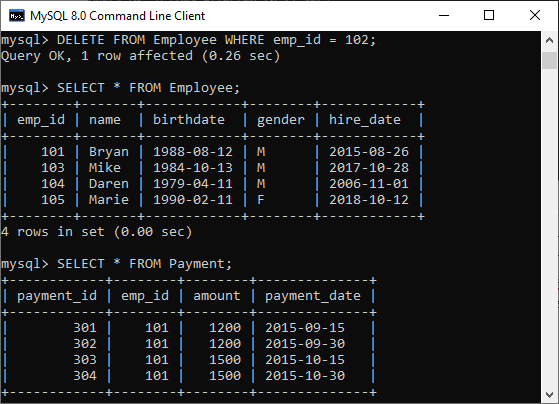
In the above output, we can see that all the rows referencing to emp_id = 102 were automatically deleted from both tables.
How to find the affected table by ON DELETE CASCADE action?
Sometimes, before deleting records from the table, we want to know the affected table by the ON DELETE CASCADE referential action. We can find this information by querying from the referential_constraints in the information_schema database as follows:
USE information_schema;
SELECT table_name FROM referential_constraints
WHERE constraint_schema = 'database_name'
AND referenced_table_name = 'parent_table'
AND delete_rule = 'CASCADE' The below statement produces the result about the tables associated with the Employee table with the ON DELETE CASCADE rule in the employeedb database:
USE information_schema;
SELECT table_name FROM referential_constraints
WHERE constraint_schema = 'employeedb'
AND referenced_table_name = 'Employee'
AND delete_rule = 'CASCADE';After executing the above command, we will get the output below:
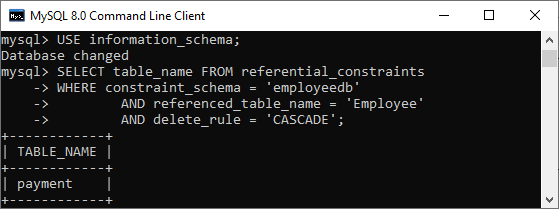
MySQL ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON UPDATE CASCADE clause in MySQL is used to update the matching records from the child table automatically when we update the rows in the parent table. The following example explains it more clearly.
First, we need to use the ALTER TABLE statement to add the ON UPDATE CASCADE clause in the table Payment as below:
ALTER TABLE Payment ADD CONSTRAINT `payment_fk`
FOREIGN KEY(emp_id) REFERENCES Employee (emp_id) ON UPDATE CASCADE; It will give the following output:
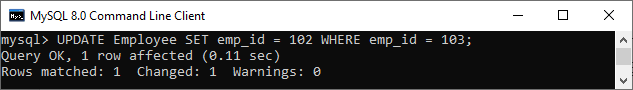
In the below script, we will update the id of the employee in the Parent Table, and it will automatically reflect this change in the child table as well:
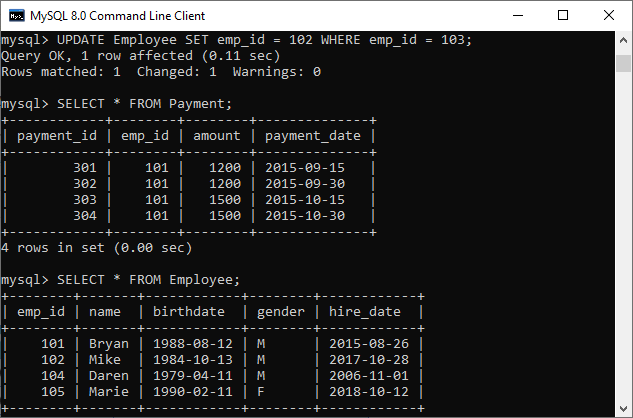
mysql> UPDATE Employee SET emp_id = 102 WHERE emp_id = 103; Verifying the content of the Employee and Payment table, we will see that emp_id column values will be updated successfully.
Leave a Reply