A comment is a programmer-readable explanation or annotation placed in the SQL queries. It is used for the purpose of making the SQL statements easier for humans to understand. MySQL generally ignores them during the parsing of the SQL code. Comments can be written in a single line or multiple lines.
MySQL can also provide an executable comment. So, until we have not to use the executable comments, it only executes the SQL part.
In MySQL Server, we can write the comments in mainly three ways that are given below:
- Using # symbol
- Using – symbol
- Using /* and */ symbol
Let us understand each in detail.
Using # symbol
It is used at the end of the line or SQL statements.
Syntax
SELECT Statement; # comment goes here Example
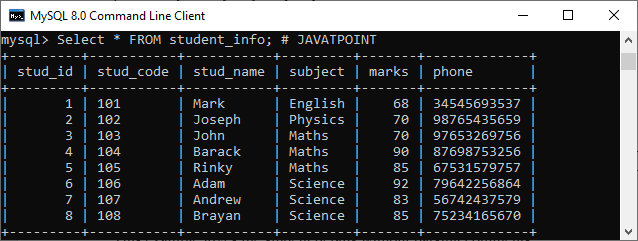
This example gives the student details without parsing comments.
Mysql> Select * FROM student_info; # JAVATPOINT Output:
Using — symbol
It is placed at the end of the line. In this comment styling, we must ensure that the double-slash has at least one whitespace or control character such as tab, space, newline, etc.
Syntax
SELECT Statement; - - comment goes here Example
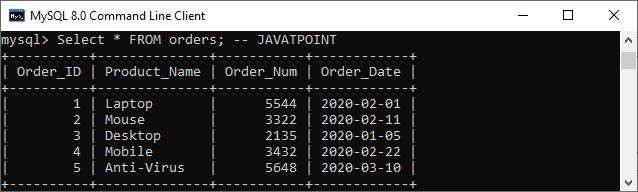
This example gives the student details without parsing comments.
mysql> SELECT * FROM orders; - - JAVATPOINT Output:
Using /* and */ symbol
This type of comment is similar to the C programming language that can span in multiple lines. We can use this comment to document the block of SQL statements.
Syntax
/*
comment goes here
comment goes here
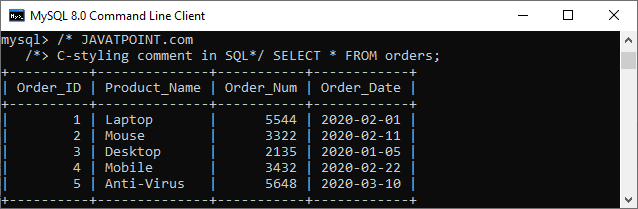
*/ /* JAVATPOINT.com
C-styling comment in SQL*/ SELECT * FROM orders;Output:
Executable Comments
MySQL has also used executable comments. This comment styling provides portability between different databases. It allows us to embed the SQL code that the only executable in MySQL, but other databases will ignore this extension.
Syntax
The following are the syntax of executable comments:
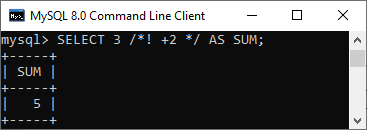
/*! MySQL-specific code */ Example
mysql> SELECT 3 /*! +2 */ AS SUM; Output:
We can also use the below syntax to execute the comment in particular version of MySQL:
/*! ##### MySQL-specific code */ Here. #### represents the MySQL version name that executes the comment. The first # used for the major version, e.g., 5 or 8. The second two ## is used for the minor version, and the last two ## used for the patch level.
Leave a Reply