The Right Join is used to joins two or more tables and returns all rows from the right-hand table, and only those results from the other table that fulfilled the join condition. If it finds unmatched records from the left side table, it returns Null value. It is similar to the Left Join, except it gives the reverse result of the join tables. It is also known as Right Outer Join. So, Outer is the optional clause used with the Right Join.
We can understand it with the following visual representation where Right Outer Join returns all records from the left-hand table and only the matching records from the other table:
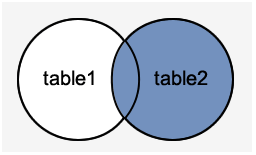
RIGHT JOIN Syntax
The following are the syntax of Right Join that joins tables Table1 and Table2:
SELECT column_list
FROM Table1
RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN Table2
ON join_condition; NOTE: In the Right Join, if the tables contain the same column name, then ON and USING clause give the equivalent results.
Let us see how Right Join works.
This Join starts selecting the columns from the right-hand table and matches each record of this table form the left table. If both records fulfill the given join condition, it combines all columns in a new row set that will be returned as output. If the rows of the right-side table do not find any matching rows form the left table, it combines those rows from the right-side table with Null values. It means, the Right Join returns all data from the right-side table weather it matches the rows form the left table or not.
MySQL RIGHT JOIN Examples
Let us take some examples to understand the working of Right Join clause:
RIGHT JOIN clause for joining two tables
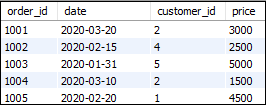
Here, we are going to create two tables “customers” and “orders” that contains the following data:
Table: customers
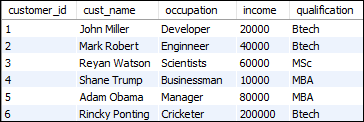
Table: orders
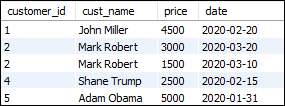
To select records from both tables using RIGHT JOIN, execute the following query:
SELECT customers.customer_id, cust_name, price, date
FROM customers
RIGHT JOIN orders ON customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id
ORDER BY customer_id; OR,
SELECT customers.customer_id, cust_name, price, date
FROM customers
RIGHT JOIN orders USING(customer_id)
ORDER BY customer_id; After successful execution of the above queries, it will give the equivalent output:
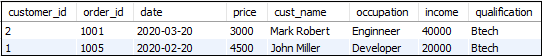
RIGHT JOIN with WHERE Clause
MySQL uses the WHERE clause to provide the filter result from the table. The following example illustrates this with the Right Join clause:
SELECT * FROM customers
RIGHT JOIN orders USING(customer_id)
WHERE price>2500 AND price<5000;This statement gives the below result:
MySQL RIGHT JOIN Multiple Tables
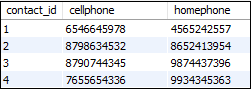
We have already created two tables, named “customers” and “orders”. Let us create one more table and name it as a “contacts” that contains the following data:
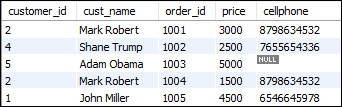
Execute the following statement to join the three table customers, orders, and contacts:
SELECT customers.customer_id, cust_name, order_id, price, cellphone
FROM customers
RIGHT JOIN contacts ON customer_id = contact_id
RIGHT JOIN orders ON customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id ORDER BY order_id; After successful execution of the above query, it will give the following output:
Use of RIGHT JOIN clause to get unmatched records
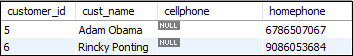
The Right Join clause is also useful in such a case when we want to get records in the table that does not contain any matching rows of data from another table.
We can understand it with the following example that uses the RIGHT JOIN clause to find a customer who has no cellphone number:
SELECT customer_id, cust_name, cellphone, homephone
FROM customers
RIGHT JOIN contacts ON customer_id = contact_id
WHERE cellphone IS NULL
ORDER BY cellphone; The above statement returns the following output:
Leave a Reply