In this section, we are going to understand the working of the PostgreSQL LIMIT clause, which is used to get a subset of rows produced by a command.
Syntax of PostgreSQL LIMIT Clause
The basic syntax of the PostgreSQL LIMIT clause is as follows:
SELECT select_list
FROM table_name
ORDER BY sort_expression
LIMIT row_countIn the above syntax, Limit clause returns row_count rows created by the command.
- If row_count value is NULL then the query will produce a similar outcome because it does not contain the LIMIT clause.
- Or if row_count is zero, the statement will return an empty set.
- We can use the OFFSET clause if we want to miss out various of rows before getting the row_count rows.
And the offset clause comes after the LIMIT clause as we can see in the below command:
SELECT select_list
FROM table_name
LIMIT row_count OFFSET row_to_skip;Note: It is an elective clause of the SELECT command, which makes the several rows returned by the query.
If we use the ORDER BY clause to have the row order with the LIMIT clause. Or if we do not use the ORDER BY clause, we may get an output with the unnamed order of rows.
Examples of PostgreSQL LIMIT
Let us see some examples to understand the working of the PostgreSQL LIMIT clause.
Here we are creating one new table called CAR with the help of the CREATE table command, and inserting some values into the CAR table using the INSERT command.
Create table CAR
(
Car_id serial not null primary Key,
Car_name VARCHAR(50),
Car_Model VARCHAR(50),
Car_Price INTEGER,
Car_Color VARCHAR(20),
BODY_Style VARCHAR(30)
);Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message window, and the CAR table has been created successfully.
After that, we are going to insert some values into the CAR table with the help of below command:
Insert into CAR
values (1001,'Acura', 'NSX', 47075, 'yellow','coupe'),
(1002,'Porche','911 Carrera', 399999, 'silver','coupe'),
(1003,'Nissan', 'Armada', 36777, 'blue','wagon'),
(1004,'Audi', 'A8', 63890,'black','sedan' ),
(1005, 'Volvo', 'XC90', 45845, 'gray','wagon'),
(1006,'BMW', 'M-Series', 108900,'red','coupe'),
(1007, 'Jaguar', 'XK', 91675, 'brown','convertible'),
(1008, 'Hummer', 'H1', 119999,'red','sedan'),
(1009, 'Mercedes-Benz','CLS Class', 86900, 'black', 'sedan'),
(1010, 'Suzuki', 'XL-7', 25880,'brown','wagon');Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message window, the values have been inserted successfully into the CAR table.
Example of constraining the number of returned rows using PostgreSQL LIMIT
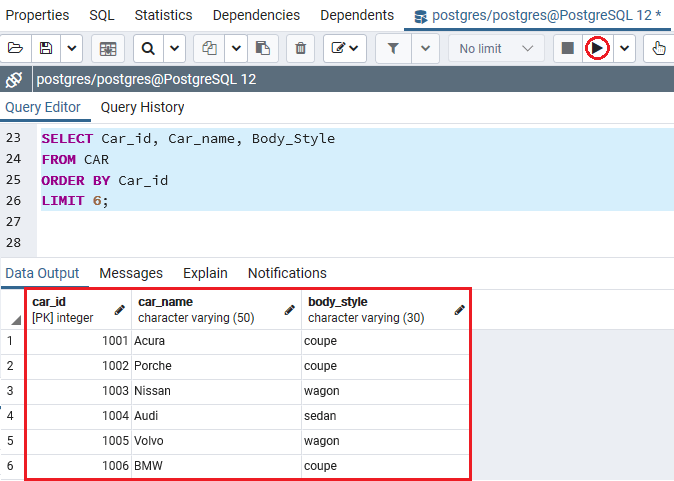
In the below example, we will fetch the first SIX CAR details sorted by Car_id with the help of the LIMIT clause.
SELECT Car_id, Car_name, Body_Style
FROM CAR
ORDER BY Car_id
LIMIT 6;After implementing the above command, we will get the below output, which displays the first six -car details into the CAR table.
Example of getting the top and bottom rows using PostgreSQL LIMIT Clause
For selecting the rows with the maximum or minimum values from a table, we often use the LIMIT clause.
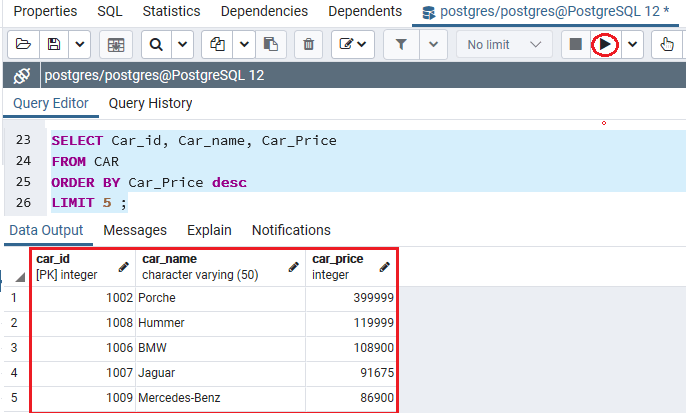
For example, if we want to sort the top five most expensive cars in terms of their price, we sort them by their Car price in descending order.
In the following command, we are using the LIMIT clause to get the most expensive cars into the CAR table:
SELECT Car_id, Car_name, Car_Price
FROM CAR
ORDER BY Car_Price desc
LIMIT 5 ;Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below output:
Example of OFFSET using PostgreSQL LIMIT clause
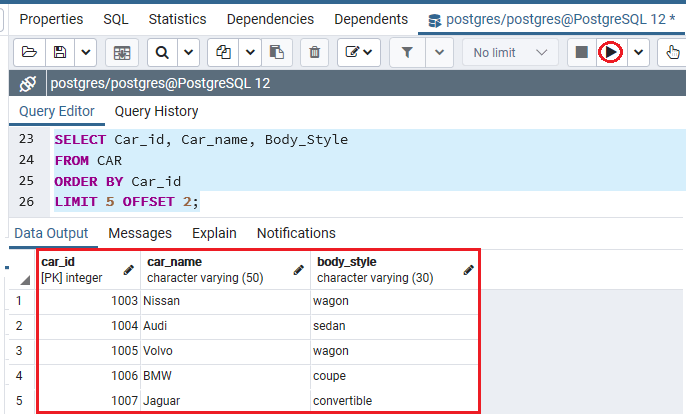
In this example, we will use LIMIT and OFFSET clauses to get five cars starting from the fifth one ordered by Car_id with the help of below command:
SELECT Car_id, Car_name, Body_Style
FROM CAR
ORDER BY Car_id
LIMIT 5 OFFSET 2;Output
After implementing the above command, we will get the below output, which displays cars from the Car_id =1003 as we put the offset values is 2, and Limit value is 5 into the CAR table.
Leave a Reply