In SQL Server, DISTINCT clause is used to remove duplicates from the table. The DISTICT clause is only used with SELECT statement.
SELECT DISTINCT expressions
FROM [database_name].[dbo].[table_name]
[WHERE conditions];Parameter explanation
expressions: It specifies the columns or calculations that you want to retrieve.
database_name & table_name: It specifies the name of the database and name of the table on which you want to do your operations.
Example:
DISTINCT clause with single expression
You have a table named “Employees”, having the following data:
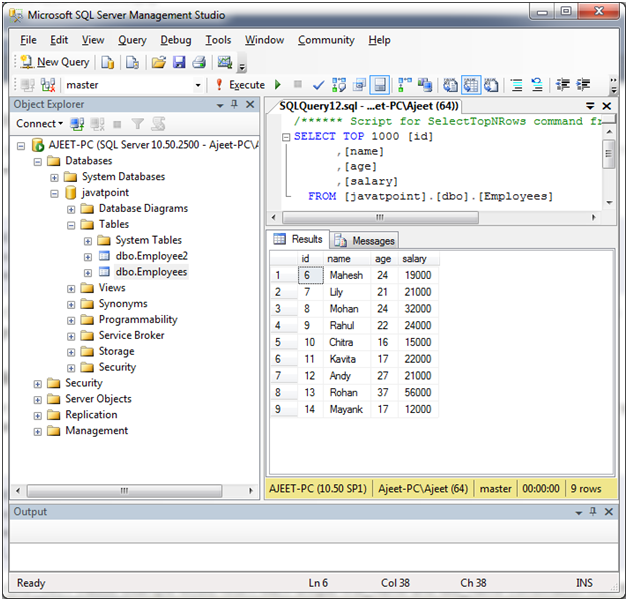
Select distinct salary from Employees where salary is greater than 12000.
SELECT DISTINCT salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE salary > 15000;Output:
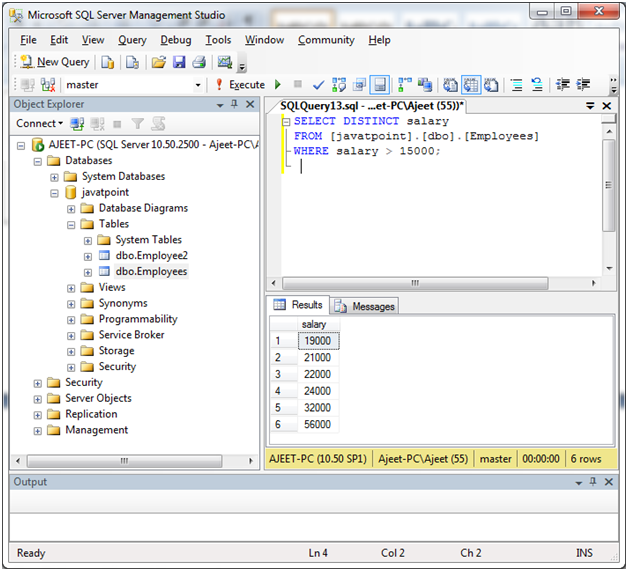
Here, you can see that there is only 6 distinct salaries within 9 records. Distinct clause shows only unique records.
DISTINCT clause with multiple expressions
DISTINCT clause can also be used with multiple expressions. It will remove duplicates from more than one field in your SELECT statement.
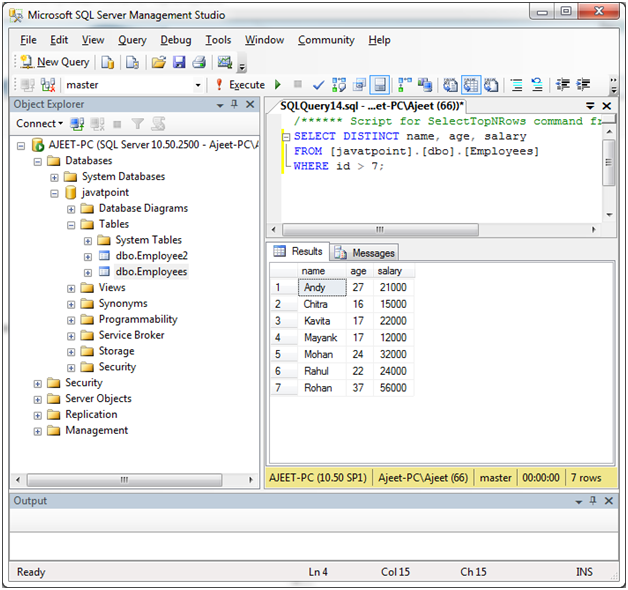
SELECT DISTINCT name, age, salary
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Employees]
WHERE id > 7;Output:
Leave a Reply