The SQL OR condition is used in SQL query to create a SQL statement where records are returned when any one condition met. It can be used in a SELECT statement, INSERT statement, UPDATE statement or DELETE statement.
Let’s see the syntax for the OR condition:
SELECT columns FROM tables WHERE condition 1 OR condition 2; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
- SQL “OR” example with SQL SELECT
This is how an SQL “OR” condition can be used in the SQL SELECT statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is IT or location is Chennai.
Query:
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp WHERE Department = "IT" OR Location = "Chennai"; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
In the emp table, there are three employees whose department is IT. But there are only two records whose location is Chennai. Still, all three records are displayed. This happened because we have specified OR operator in the query, according to which the record will be considered in the result set even any one condition is met.
Example 2:
Write a query to get the records from emp tables in which department of the employee is Marketing or location is Noida.
Query:
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp WHERE Department = "Marketing" OR Location = "Noida"; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
There are two employees whose department is Marketing in the emp table, but still, three records are displayed. This happened because of the use of the OR operator in the query. Among the three records displayed above, the first two records satisfy condition 1; the second record satisfies both the conditions and the third record satisfies only condition 1. Due to the OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, the record is considered in the result-set.
- SQL “OR” example with SQL UPDATE
This is how the “OR” condition can be used in the SQL UPDATE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to update the records in emp tables in which department of the employee is Marketing, or the last name is Tarle. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the location as Delhi.
Query:
mysql> UPDATE emp SET Location = "Delhi" WHERE Department = "Marketing" OR Last_Name = "Tarle"; 
We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | Finance | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | Finance | Bangalore |
There are two employees whose department is ‘Marketing’ and one record whose last name is ‘Tarle’ in the emp table. Though only one condition is still met, that record is considered and updated in the table due to the OR operator.
Example 2:
Write a query to update the records in the emp table in which department of the employee is Finance, or the first name is Sandhya. For that particular employee, set the updated value of the department as HR.
Query:
mysql> UPDATE emp SET Department = "HR" WHERE Department = "Finance" OR First_Name = "Sandhya"; 
We will use the SELECT query to verify the updated record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Delhi |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Delhi |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Delhi |
| 6 | Roshni | Jadhav | HR | Bangalore |
| 7 | Sandhya | Jain | HR | Noida |
There are two employees whose department is ‘Finance,’ and among these two records, one record satisfies both the conditions in the emp table. However, both the records are considered and updated in the table due to the OR operator.
- SQL “OR” example with SQL DELETE
This is how an SQL “OR” condition can be used in the SQL DELETE statement.
Example 1:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which the last name of the employee is Jain or Location is Bangalore.
Query:
mysql> DELETE FROM emp WHERE Last_Name = 'Jain' OR Location = 'Bangalore'; 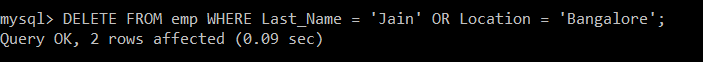
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harshad | Kuwar | Marketing | Pune |
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 3 | Chaitali | Tarle | IT | Chennai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
| 5 | Suraj | Tripathi | Marketing | Pune |
There is only one record in the emp table whose last name is Jain and one record whose location is Bangalore. But still, due to the presence of an OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, that particular record is deleted.
Example 2:
Write a query to delete the records from the emp table in which department of the employee is marketing and Location is Delhi.
Query:
mysql> DELETE FROM emp WHERE Department = 'Marketing' OR Location = 'Delhi'; 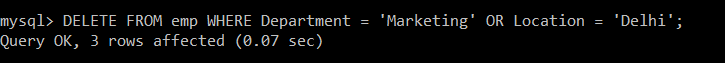
We will use the SELECT query to verify the deleted record.
mysql> SELECT *FROM emp; | ID | First_Name | Last_Name | Department | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anurag | Rajput | IT | Mumbai |
| 4 | Pranjal | Patil | IT | Chennai |
There is only one record in the emp table whose department is Marketing and one record whose location is Delhi. But still, due to the presence of an OR operator, even if anyone condition is satisfied, that particular record is deleted.
Leave a Reply