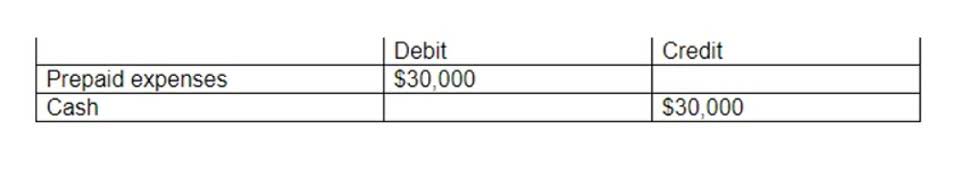
Once journal entries are made in the general journal or subsidiary journals, they must be posted and transferred to the T-accounts or ledger accounts. The left side of the T-account is for debits, and the right side is for credits. In double-entry accounting, debits and credits always need to balance out. While you are in a course like accounting basics, T accounts are a fantastic way to grasp the debits and credits visually. It’s true that you can make a T account for any account but let’s take an account like cash.

Rent Expense Account
In this example, the column balances are tallied, so you can understand how the T-accounts work. The account balances are calculated by adding the payroll debit and credit columns together. This sum is typically displayed at the bottom of the corresponding side of the account. Reconciliation compares T account balances with external records, such as bank statements or subsidiary ledgers.
- They help you keep track of adjusting entries and see how they affect your income statement.
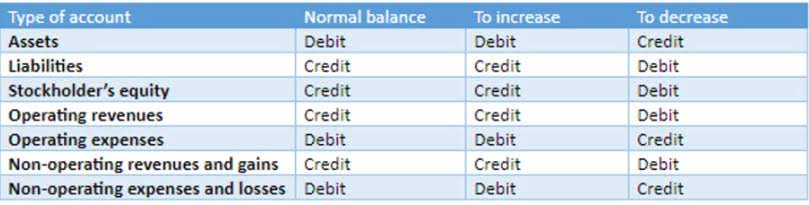
- In accounting, however, debits and credits refer to completely different things.
- T-accounts show you what to put in the ledger to keep everything balanced.
- In other words, an account with a credit balance will have a total on the bottom of the right side of the account.
- As you can see, it’s basically a mirror image of what we recorded in the Bank T account.
- If transactions are recorded incorrectly in a T-account, the mistake carries over to financial reports.
- It is impossible to provide a complete set of examples that address every variation in every situation since there are hundreds of such T-accounts.
We and our partners process data to provide:
After assessing what debit and credit entry applies to each specific account, T accounts can be created. If transactions are recorded incorrectly in a T-account, the mistake carries over to financial reports. You can see the specific date, the description of the transaction and a running balance beside the debits and credits. T-accounts can display transactions from a specific time period such as a week or a month. By displaying multiple transactions over a time period rather than a single transaction, it allows people to see a picture of a company’s activities. T-accounts are used to track debits and credits made to an account.
- The visual representation can be easier for beginners than just putting them straight in a line.
- When looking to assess your business’ financial performance, one of the most important metrics to keep in mind is EBIT (Earnings Before Interest…
- After assessing what debit and credit entry applies to each specific account, T accounts can be created.
- This transaction will decrease ABC’s Cash account by $5,000, and its liability Notes Payable account will also decrease by $5,000.
- To find the account balance, subtract the total debits from the total credits.
What are T Accounts?

For more examples and applications, explore our sections on journal entry and t accounts. Equity T accounts capture t accounts the residual interest in a company’s assets after deducting liabilities, including common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital. For example, when a company issues 1,000 shares at $10 each, the cash account is debited by $10,000, and the common stock account is credited by the same amount. Retained earnings reflect net income and dividends, directly influencing equity. Understanding equity accounts is essential for calculating return on equity (ROE), which measures profitability by comparing net income to shareholders’ equity.

- Think of it as a financial X-ray, giving loan officers a glimpse into the inner workings of a business.
- The ingredients for the cup of coffee are recorded as inventory (asset account).
- For new accounting students raised on software, T accounts provide a familiar and intuitive way to grasp the underlying logic of accounting.
- Consequently, businesses employing accrual accounting methods may find T-accounts insufficient for accurately reflecting their financial position and performance.
- T-accounts alone may obscure vital details, such as foreign exchange gains or losses, derivatives, and intercompany transactions.
- Depreciation, calculated using methods like the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), reduces the asset’s book value over time.
- This helps you understand your revenue stream and make informed decisions about your business.
And if you’re new to the accounting world and have little knowledge in finance, T accounts can be especially useful Car Dealership Accounting in working through complex financial transactions. The use and purpose of a T account is to help business owners visualize the amounts on each individual account. Splitting out debits and credits makes it easier to quickly spot things when looking at the ledger.
- We will look at what T accounts are and how to use them so you can grasp accounting easier.
- Using T-accounts to record such transactions may obscure the timing and matching of revenue and expenses, leading to inaccurate financial statements.
- So, when you borrow money from the bank (debiting cash, which is an asset), you’re also increasing your liabilities (debit).
- A T Account is the visual structure used in double entry bookkeeping to keep debits and credits separated.
- Debits and credits are the foundation of recording financial transactions.
Leave a Reply