The SELECT statement in MySQL is used to fetch data from one or more tables. We can retrieve records of all fields or specified fields that match specified criteria using this statement. It can also work with various scripting languages such as PHP, Ruby, and many more.
SELECT Statement Syntax
It is the most commonly used SQL query. The general syntax of this statement to fetch data from tables are as follows:
SELECT field_name1, field_name 2,... field_nameN
FROM table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY field_name(s)]
[HAVING condition]
[ORDER BY field_name(s)]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N];Syntax for all fields:
SELECT * FROM tables [WHERE conditions]
[GROUP BY fieldName(s)]
[HAVING condition]
[ORDER BY fieldName(s)]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N];Parameter Explanation
The SELECT statement uses the following parameters:
| Parameter Name | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| field_name(s) or * | It is used to specify one or more columns to returns in the result set. The asterisk (*) returns all fields of a table. |
| table_name(s) | It is the name of tables from which we want to fetch data. |
| WHERE | It is an optional clause. It specifies the condition that returned the matched records in the result set. |
| GROUP BY | It is optional. It collects data from multiple records and grouped them by one or more columns. |
| HAVING | It is optional. It works with the GROUP BY clause and returns only those rows whose condition is TRUE. |
| ORDER BY | It is optional. It is used for sorting the records in the result set. |
| OFFSET | It is optional. It specifies to which row returns first. By default, It starts with zero. |
| LIMIT | It is optional. It is used to limit the number of returned records in the result set. |
NOTE: It is to note that MySQL always evaluates the FROM clause first, and then the SELECT clause will be evaluated.
MySQL SELECT Statement Example:
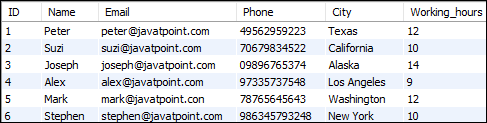
Let us understand how SELECT command works in MySQL with the help of various examples. Suppose we have a table named employee_detail that contains the following data:
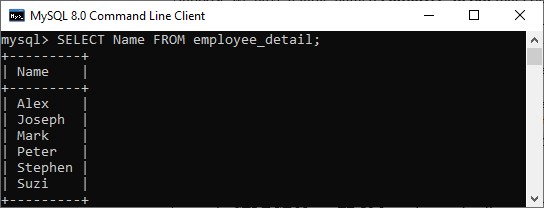
1. If we want to retrieve a single column from the table, we need to execute the below query:
mysql> SELECT Name FROM employee_detail; We will get the below output where we can see only one column records.
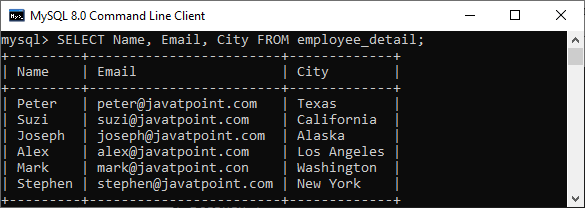
2. If we want to query multiple columns from the table, we need to execute the below query:
mysql> SELECT Name, Email, City FROM employee_detail; We will get the below output where we can see the name, email, and city of employees.
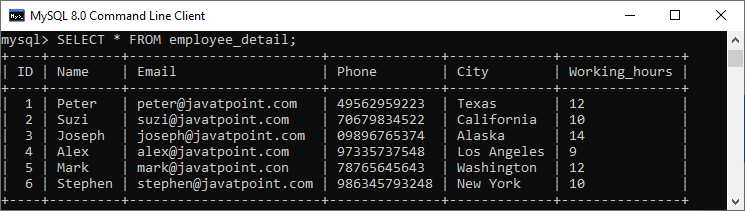
3. If we want to fetch data from all columns of the table, we need to use all column’s names with the select statement. Specifying all column names is not convenient to the user, so MySQL uses an asterisk (*) to retrieve all column data as follows:
mysql> SELECT * FROM employee_detail; We will get the below output where we can see all columns of the table.
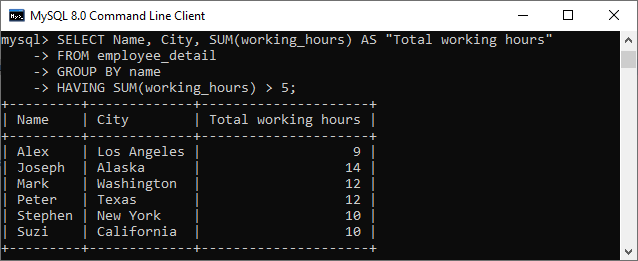
4. Here, we use the SUM function with the HAVING clause in the SELECT command to get the employee name, city, and total working hours. Also, it uses the GROUP BY clause to group them by the Name column.
SELECT Name, City, SUM(working_hours) AS "Total working hours"
FROM employee_detail
GROUP BY Name
HAVING SUM(working_hours) > 5;It will give the below output:
5. MySQL SELECT statement can also be used to retrieve records from multiple tables by using a JOIN statement. Suppose we have a table named “customer” and “orders” that contains the following data:
Table: customer
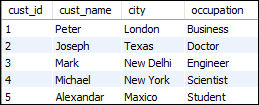
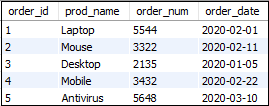
Table: orders
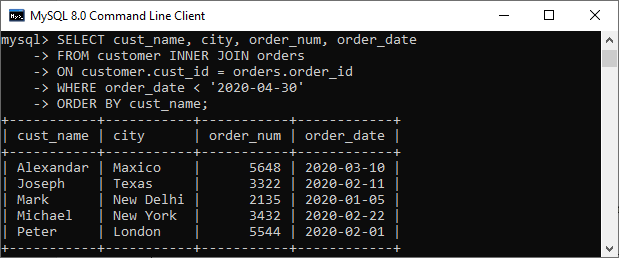
Execute the following SQL statement that returns the matching records from both tables using the INNER JOIN query:
SELECT cust_name, city, order_num, order_date
FROM customer INNER JOIN orders
ON customer.cust_id = orders.order_id
WHERE order_date < '2020-04-30'
ORDER BY cust_name;After successful execution of the query, we will get the output as follows:
Leave a Reply