A list of all important Date and Time related functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| AGE() | Subtract arguments |
| CURRENT DATE/TIME() | It specifies current date and time. |
| DATE_PART() | Get subfield (equivalent to extract) |
| EXTRACT() | Get subfield. |
| ISFINITE() | Test for finite date ,time and interval (not +/-infinity) |
| JUSTIFY | Adjust interval |
AGE(timestamp, timestamp) & AGE(timestamp):
| function | description |
|---|---|
| age(timestamp, timestamp) | when invoked with the timestamp form of the second argument, age() subtract arguments, producing a “symbolic” result that uses years and months and is of type interval. |
| age(timestamp) | when invoked with only the timestamp as argument, age() subtracts from the current_date (at midnight). |
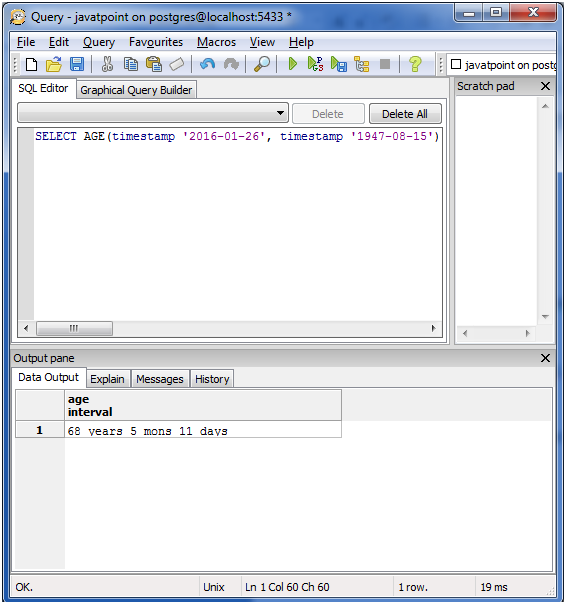
Let’s take an example to check the AGE(timestamp, timestamp) query.
See this example:
Open query page by pressing Ctrl+E.
Execute this query:
SELECT AGE(timestamp ‘2016-01-26’, timestamp ‘1947-08-15’);
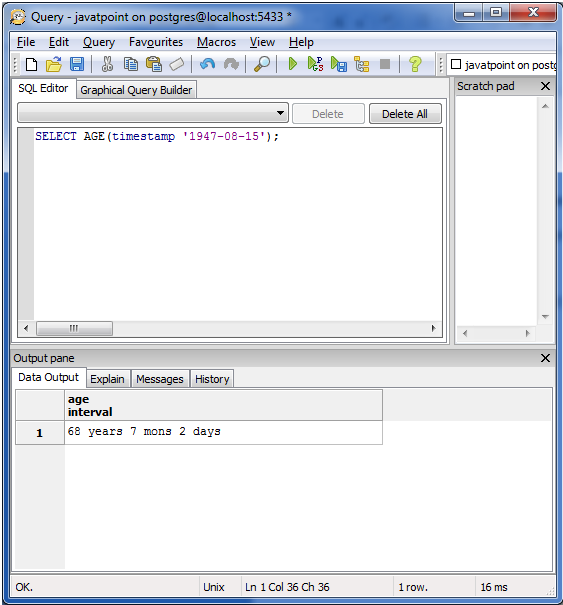
Example for function AGE(timestamp) is:
It is used to produce the current age.
Execute the following query:
SELECT AGE(timestamp ‘1947-08-15’);
Current DATE/TIME()
Following is a list of functions that return values related to the current date and time.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| CURRENT_DATE | Delivers current date. |
| CURRENT_TIME | Delivers values with time zone. |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | Delivers values with time zone. |
| CURRENT_TIME(precision) | Optionally takes a precision parameter, which causes the result to be rounded to that many fractional digits in the seconds field. |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(precision) | Optionally takes a precision parameter, which causes the result to be rounded to that many fractional digits in the seconds field. |
| LOCALTIME | Delivers values without time zone. |
| LOCALTIMESTAMP | Delivers values without time zone. |
| LOCALTIME(precision) | Optionally takes a precision parameter, which causes the result to be rounded to that many fractional digits in the seconds field. |
| LOCALTIMESTAMP(precision) | Optionally takes a precision parameter, which causes the result to be rounded to that many fractional digits in the seconds field. |
Now, you can check the following commands:
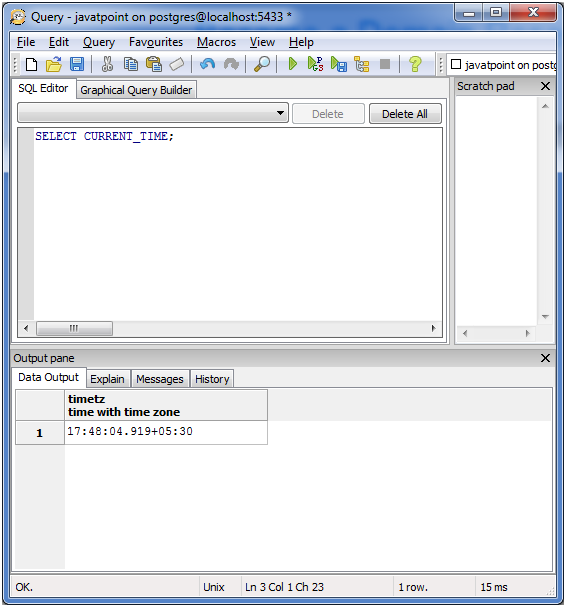
For current time:
SELECT CURRENT_TIME;
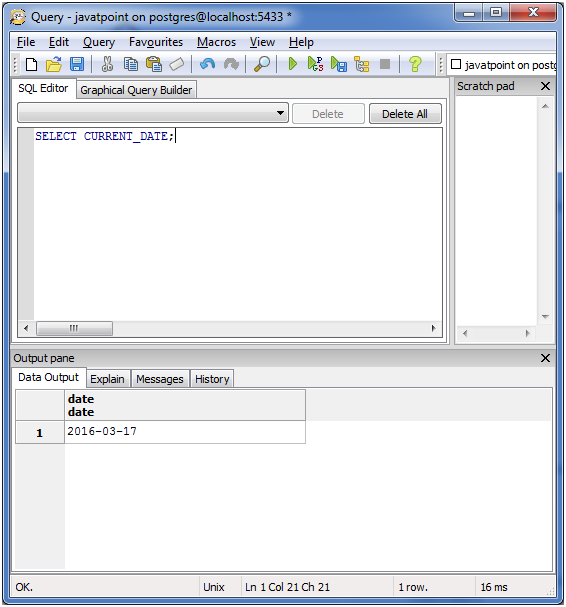
For current date:
SELECT CURRENT_DATE;
For current timestamp (date and time both)
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
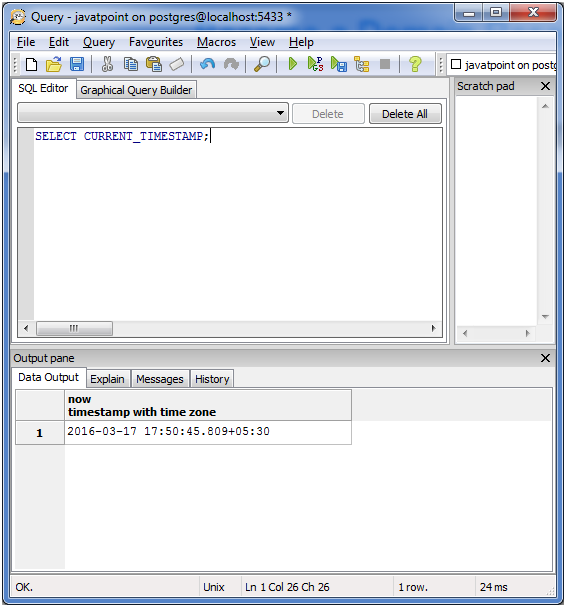
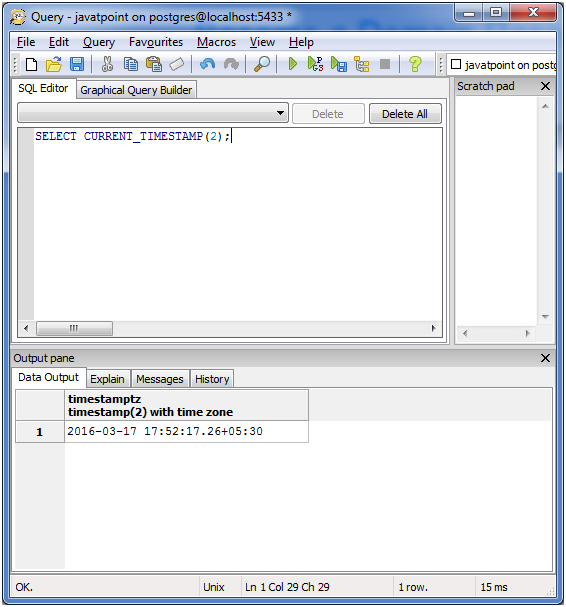
Current timestamp with more precision:
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(2);
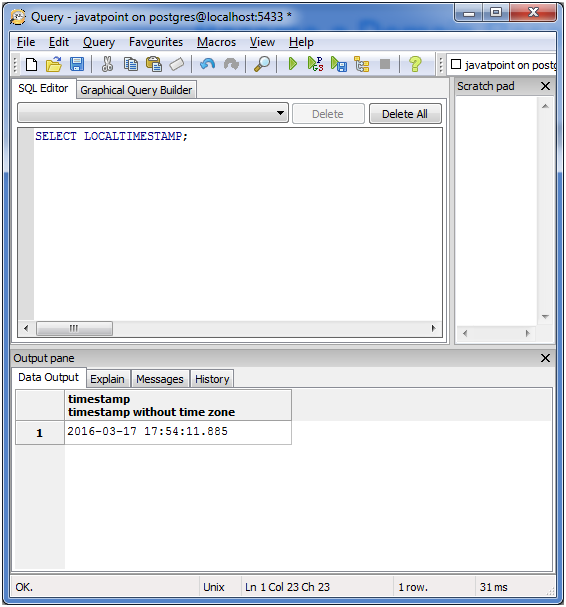
Local Timestamp:
SELECT LOCALTIMESTAMP;
Leave a Reply