MySQL ALTER statement is used when you want to change the name of your table or any table field. It is also used to add or delete an existing column in a table.
The ALTER statement is always used with “ADD”, “DROP” and “MODIFY” commands according to the situation.
1) ADD a column in the table
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD new_column_name column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ];Parameters
table_name: It specifies the name of the table that you want to modify.
new_column_name: It specifies the name of the new column that you want to add to the table.
column_definition: It specifies the data type and definition of the column (NULL or NOT NULL, etc).
FIRST | AFTER column_name: It is optional. It tells MySQL where in the table to create the column. If this parameter is not specified, the new column will be added to the end of the table.
Example:
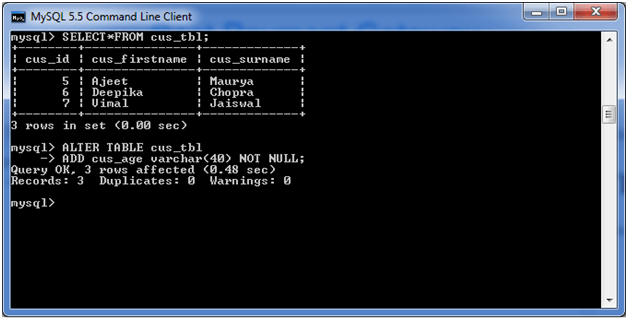
In this example, we add a new column “cus_age” in the existing table “cus_tbl”.
Use the following query to do this:
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
ADD cus_age varchar(40) NOT NULL;Output:
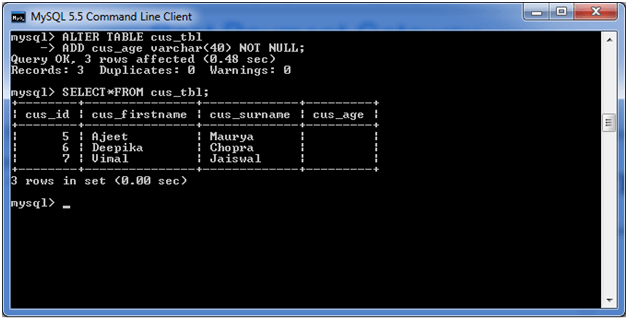
See the recently added column:
SELECT* FROM cus_tbl;Output:
2) Add multiple columns in the table syntax
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD new_column_name column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ],
ADD new_column_name column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ],
...
; Example:
In this example, we add two new columns “cus_address”, and cus_salary in the existing table “cus_tbl”. cus_address is added after cus_surname column and cus_salary is added after cus_age column.
Use the following query to do this:
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
ADD cus_address varchar(100) NOT NULL
AFTER cus_surname,
ADD cus_salary int(100) NOT NULL
AFTER cus_age ;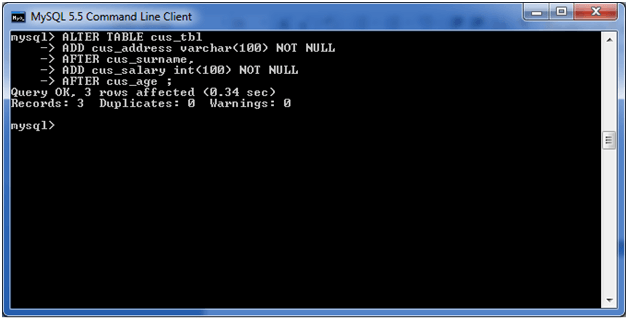
SELECT* FROM cus_tbl;
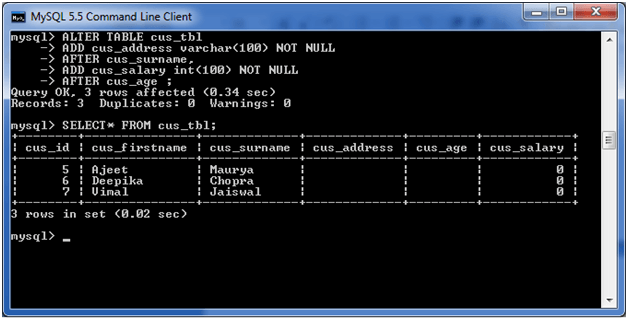
3) MODIFY column in the table
The MODIFY command is used to change the column definition of the table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY column_name column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ];Example:
In this example, we modify the column cus_surname to be a data type of varchar(50) and force the column to allow NULL values.
Use the following query to do this:
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
MODIFY cus_surname varchar(50) NULL;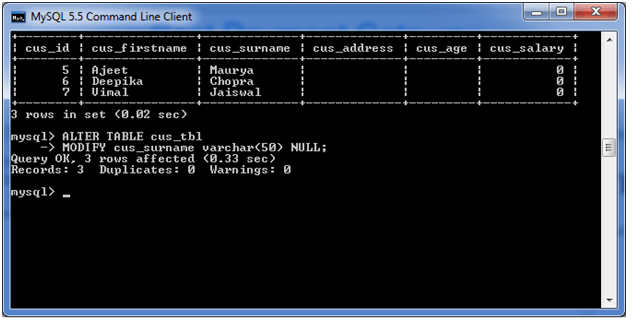
See the table structure:
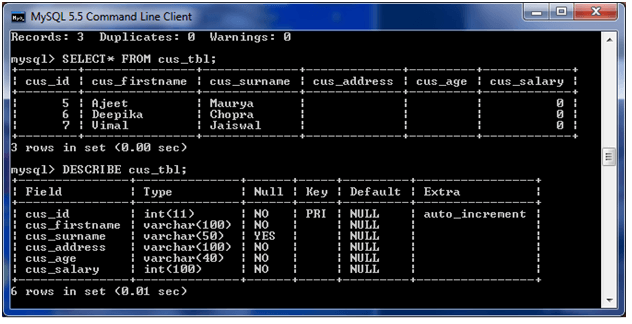
4) DROP column in table
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
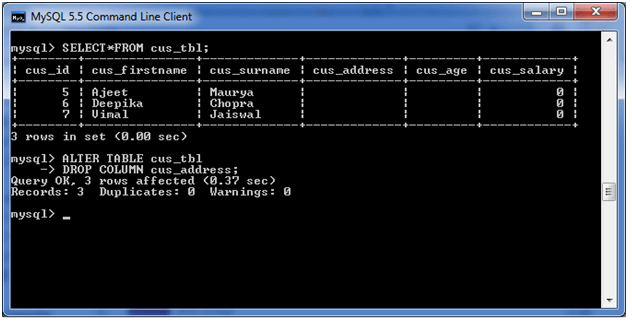
DROP COLUMN column_name;Let’s take an example to drop the column name “cus_address” from the table “cus_tbl”.
Use the following query to do this:
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
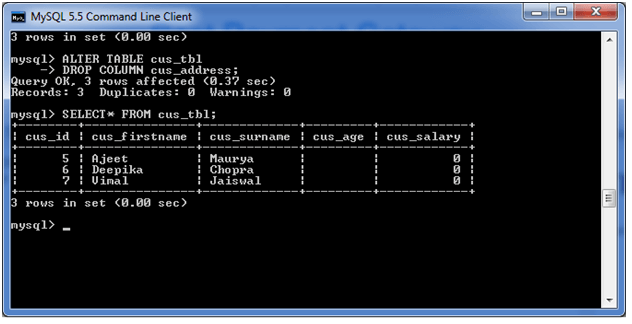
DROP COLUMN cus_address; Output:
See the table structure:
5) RENAME column in table
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
CHANGE COLUMN old_name new_name
column_definition
[ FIRST | AFTER column_name ]Example:
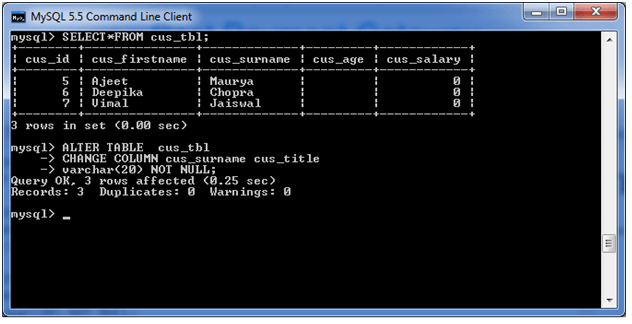
In this example, we will change the column name “cus_surname” to “cus_title”.
Use the following query to do this:
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
CHANGE COLUMN cus_surname cus_title
varchar(20) NOT NULL;Output:
6) RENAME table
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME TO new_table_name;Example:
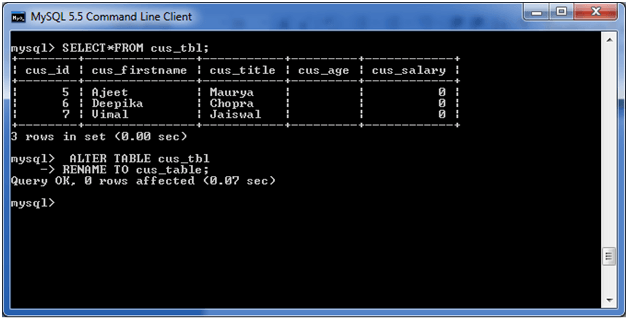
In this example, the table name cus_tbl is renamed as cus_table.
ALTER TABLE cus_tbl
RENAME TO cus_table;
Output:
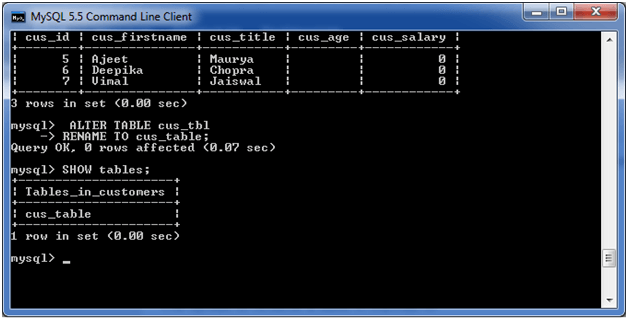
See the renamed table:
Leave a Reply