MySQL Limit query is used to restrict the number of rows returns from the result set, rather than fetching the whole set in the MySQL database. The Limit clause works with the SELECT statement for returning the specified number of rows only. This query accepts only one or two arguments, and their values should be zero or any positive integer.
It is essential in such a case when the table contains thousands of rows, or you want to return only the recently inserted data. In other words, if you are not interested in getting all the rows returned from the query, use the MySQL Limit clause with the SELECT statement. It improves the performance of the query and even stops having crashed the system when the table contains a large number of data.
To get only the specified rows from the table, MySQL uses the LIMIT clause, whereas SQL uses the TOP clause, and Oracle uses the ROWNUM clause with the SELECT statement.
Syntax
The following are the syntax of using Limit query in MySQL:
SELECT column_list
FROM table_name
LIMIT offset, count;In the above syntax, we can see:
Column_list: It is the name of the column that you want to return.
Table_name: It is the name of the table that contains your column name.
Offset: It specifies the number of a row from which you want to return. The offset of the row starts from 0, not 1.
Count: It specifies the maximum number of rows you want to return.
The following visual representation explains it more clearly:
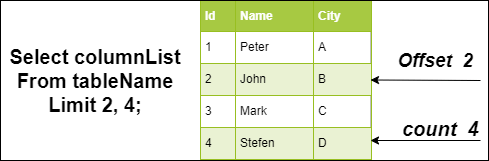
NOTE: If you specify only one argument with the Limit clause, MySQL assumes this to determine the maximum number of rows for returning output from the result set. In that case, Limit clause arguments, offset, and the count is equivalent.
LIMIT Clause with ORDER BY Clause
The user needs to use the Limit clause with the Order By clause. Without using Order By clause, you will get the result in an unspecified order. In that case, it is tough to know the query returns result from which rows. So, it is a good habit to use Group By clause with a Limit clause for getting the rows in a specific order.
The following syntax can be used to get the result in a unique order:
SELECT column_list
FROM table_name
GROUP BY order_expression
LIMIT offset, count;MySQL Limit Examples
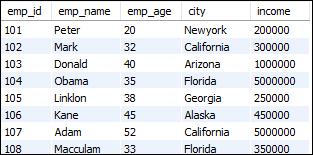
Let us create a sample table in the database that contains the following data and understand how Limit clause works in MySQL using various examples:
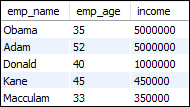
Table: employees
1. MySQL Limit to return highest or lowest rows
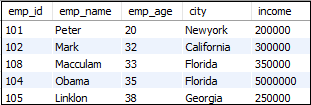
The following statement used to get the top five younger employees:
SELECT * FROM employees
ORDER BY emp_age
LIMIT 5;This statement first sorts the employee age using Group By clause, and then the Limit clause returns the top-five result. After executing the above steps, we will get the following output:
2. MySQL Limit to get a range of rows using offset
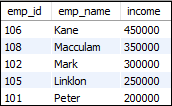
Sometimes you want to get a result between the ranges of values. For example, you have a large number of rows to display data on applications, then divide it into pages, and each page contains a maximum of 10 rows in a table. In that case, you can use the following query to get a range of rows:
SELECT emp_id, emp_name, income FROM employees
ORDER BY income DESC
LIMIT 3,7; This statement returns the rows starting from row number 3 and goes to a maximum of 7th rows. It also sorts the income of the employee in highest to lowest orders. Execute the query, and you will get the following output:
3. MySQL Limit with WHERE Clause
MySQL Limit can also be worked with WHERE clause. It first checks the specified condition in the table and produces the rows that matched the condition.
This query selects the first five employees whose age is greater than 30. Here, we also used the Order By clause to sort the employees in a descending order using their income.
SELECT emp_name, emp_age, income FROM employees
WHERE emp_age>30
ORDER BY income DESC
LIMIT 5; After successful execution of the above statement, we will get the following output:
4. MySQL LIMIT to get the nth highest or lowest value
Sometimes we want to get the rows of nth highest or lowest value. In that case, we can use the following MySQL LIMIT clause to get the expected result:
SELECT column_list
FROM table_name
ORDER BY expression
LIMIT n-1, 1;In this syntax, the LIMIT n-1, 1 clause returns 1 row that starts at the row n.
For example, the following query returns the employee information who has the second-highest income:
SELECT emp_name, city, income FROM employees
ORDER BY income
LIMIT 1, 1; Executing the above statement, it will give the following query:

It is to be noted that the above query only works when your table does not contains two employees who have some income. In that case, we will use DENSE_RANK () to get a more accurate result.
Leave a Reply