The AFTER DELETE Trigger in MySQL is invoked automatically whenever a delete event is fired on the table. In this article, we are going to learn how to create an AFTER DELETE trigger with its syntax and example.
Syntax
The following is the syntax to create an AFTER DELETE trigger in MySQL:
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
AFTER DELETE
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
Trigger_body ; The AFTER DELETE trigger syntax parameter can be explained as below:
- First, we will specify the name of the trigger that we want to create. It should be unique within the schema.
- Second, we will specify the trigger action time, which should be AFTER DELETE. This trigger will be invoked after each row of alterations occurs on the table.
- Third, we will specify the name of a table to which the trigger is associated. It must be written after the ON keyword. If we did not specify the table name, a trigger would not exist.
- Finally, we will specify the trigger body that contains a statement for execution when the trigger is activated.
If we want to execute multiple statements, we will use the BEGIN END block that contains a set of SQL queries to define the logic for the trigger. See the below syntax:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name AFTER DELETE
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
variable declarations
trigger code
END$$
DELIMITER ; Restrictions
- We can access the OLD rows but cannot update them in the AFTER DELETE trigger.
- We cannot access the NEW rows. It is because there are no NEW row exists.
- We cannot create an AFTER DELETE trigger on a VIEW.
AFTER DELETE Trigger Example
Let us understand how to create an AFTER DELETE trigger using the CREATE TRIGGER statement in MySQL with an example.
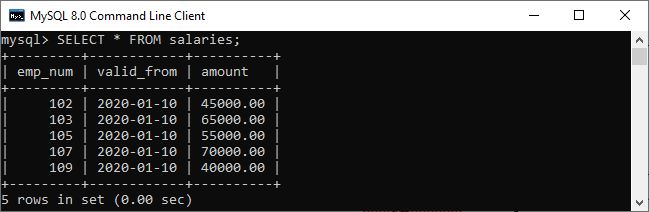
Suppose we have created a table named salaries to store the salary information of an employee as follows:
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_num INT PRIMARY KEY,
valid_from DATE NOT NULL,
amount DEC(8 , 2 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
); Next, we will insert some records into this table using the below statement:
INSERT INTO salaries (emp_num, valid_from, amount)
VALUES
(102, '2020-01-10', 45000),
(103, '2020-01-10', 65000),
(105, '2020-01-10', 55000),
(107, '2020-01-10', 70000),
(109, '2020-01-10', 40000); Execute the SELECT query to see the table data.
Third, we will create another table named total_salary_budget that keeps the salary information from the salaries table.
CREATE TABLE total_salary_budget(
total_budget DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL
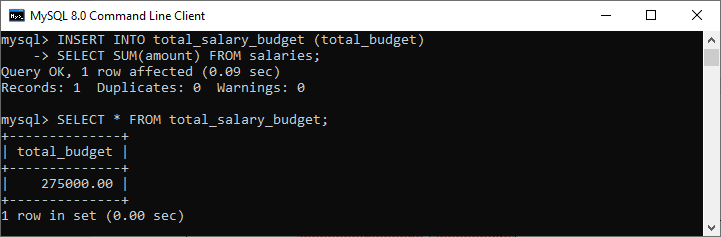
); Fourth, we will use the SUM() function that returns the total salary from the salaries table and keep this information in the total_salary_budget table:
mysql> INSERT INTO total_salary_budget (total_budget)
SELECT SUM(amount) FROM salaries;Execute the SELECT statement to verify the table:
We will then create an AFTER DELETE trigger that updates the total salary into the total_salary_budget table after a row is deleted from the salaries table.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER after_delete_salaries
AFTER DELETE
ON salaries FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
UPDATE total_salary_budget SET total_budget = total_budget - old.amount;
END$$
DELIMITER ; 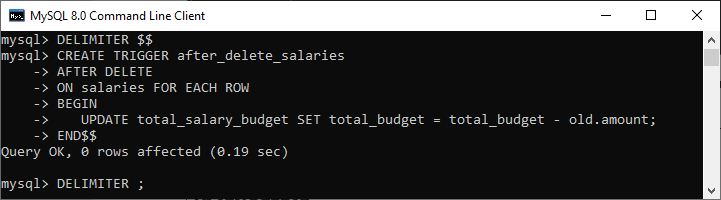
In this trigger, we have first specified the trigger name after_delete_salaries. Then, specify the triggering event. Third, we have specified the table name on which the trigger is associated. Finally, we have written the trigger logic inside the trigger body that updates the total salary into the total_salary_budget table after a row is deleted from the salaries table.
How to call the AFTER DELETE trigger?
First, we will delete a salary from the salaries table using the following statements to invoke the above-created trigger:
mysql> DELETE FROM salaries WHERE emp_num = 105; Next, we will query data from the total_salary_budget table. We can see that table has been modified after the execution of the query. See the below output:
mysql> SELECT * FROM total_salary_budget; 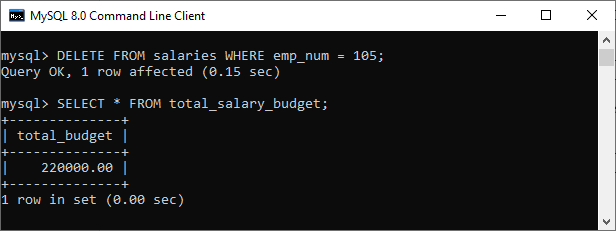
In the output, we can see that the deleted salary reduces the total_budget.
Third, we will remove all data from the salaries table:
mysql> DELETE FROM salaries; Again, we will query data from the total_salary_budget table. We can see that the trigger updated the table to zero after the execution of the query. See the below output:
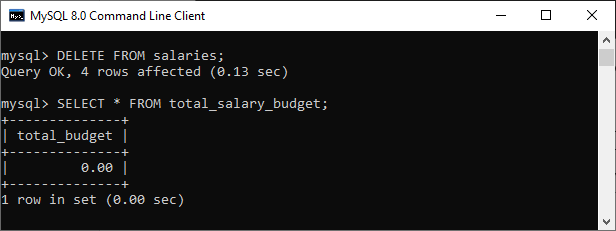
How to create AFTER DELETE Trigger in MySQL workbench?
To create an after insert trigger using this tool, we first need to launch the MySQL Workbench and log in using the username and password we have created earlier. We will get the screen as follows:
Now do the following steps for creating an AFTER DELETE trigger:
1. Go to the Navigation tab and click on the Schema menu that contains all the databases available in the MySQL server.
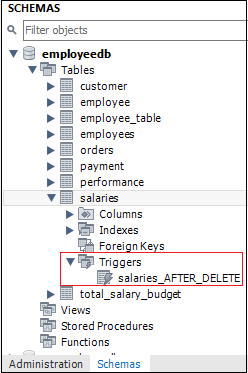
2. Select the database (for example, employeedb), double click on it that shows the sub-menu containing Tables, Views, Functions, and Stored Procedures. See the below screen.
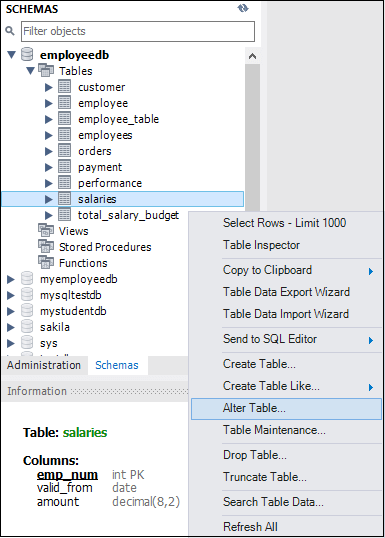
3. Expand the Tables sub-menu and select the table on which you want to create a trigger. After selecting a table, right-click on the selected table (for example, salaries), and then click on the Alter Table option. See the below image:
4. Clicking on the Alter Table option gives the screen as below:
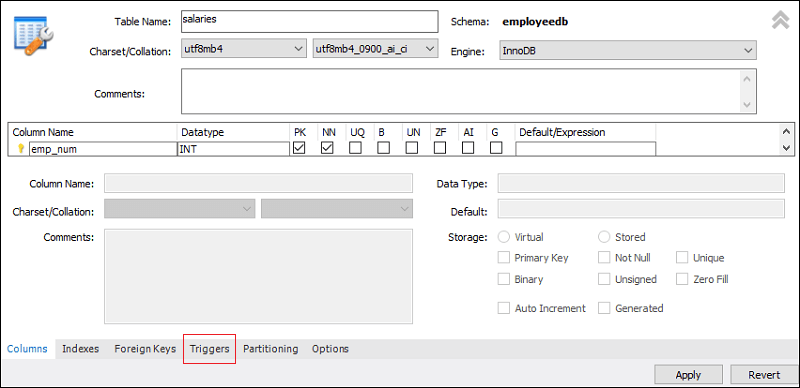
5. Now, click on the Trigger tab shown in the previous section’s red rectangular box, then select the Timing/Event AFTER DELETE. We will notice that there is a (+) icon button to add a trigger. Clicking on that button, we will get a default code on the trigger based on choosing Timing/Event:
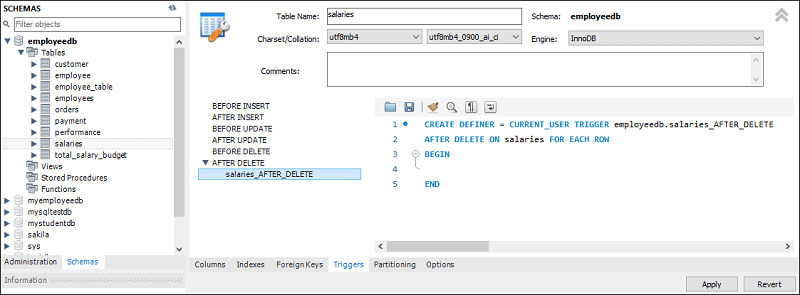
6. Now, complete the trigger code, review them once again, and if no error is found, click on the Apply button.
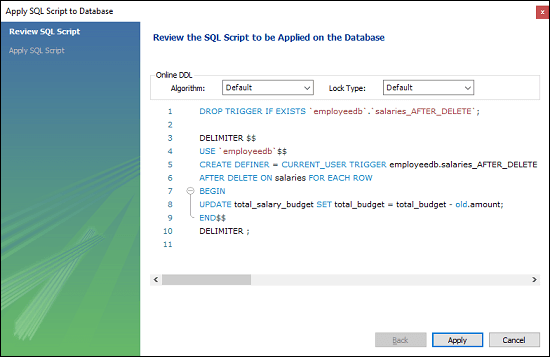
7. After clicking on the Apply button, click on the Finish button for completion.
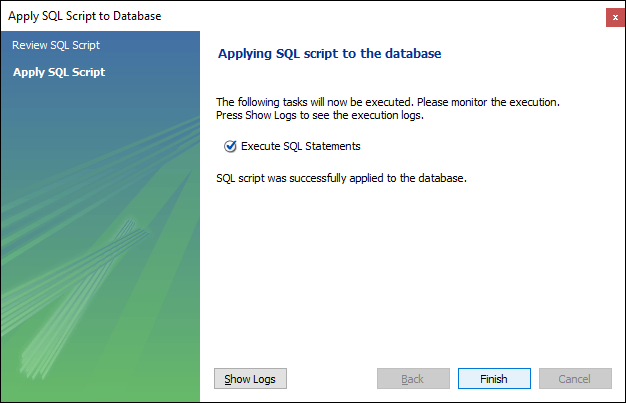
8. If we look at the schema menu, we can see salaries_AFTER_DELETE trigger under the salaries table as follows:
Leave a Reply