In MySQL, LIKE condition is used to perform pattern matching to find the correct result. It is used in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE statement with the combination of WHERE clause.
Syntax:
expression LIKE pattern [ ESCAPE 'escape_character' ] Parameters
expression: It specifies a column or field.
pattern: It is a character expression that contains pattern matching.
escape_character: It is optional. It allows you to test for literal instances of a wildcard character such as % or _. If you do not provide the escape_character, MySQL assumes that “\” is the escape_character.
MySQL LIKE Examples
1) Using % (percent) Wildcard:
Consider a table “officers” having the following data.
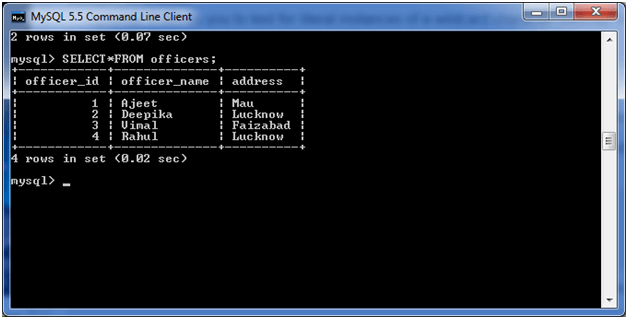
Execute the following query:
SELECT officer_name
FROM officers
WHERE address LIKE 'Luck%'; Output:
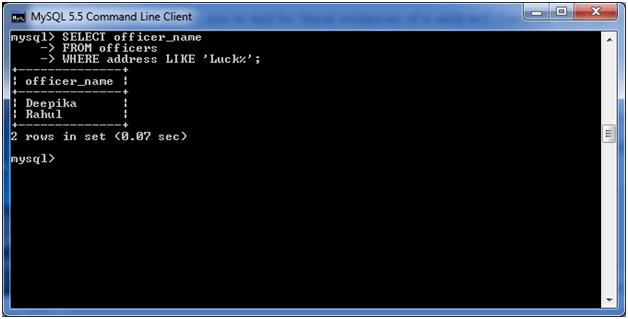
2) Using _ (Underscore) Wildcard:
We are using the same table “officers” in this example too.
Execute the following query:
SELECT officer_name
FROM officers
WHERE address LIKE 'Luc_now'; Output:
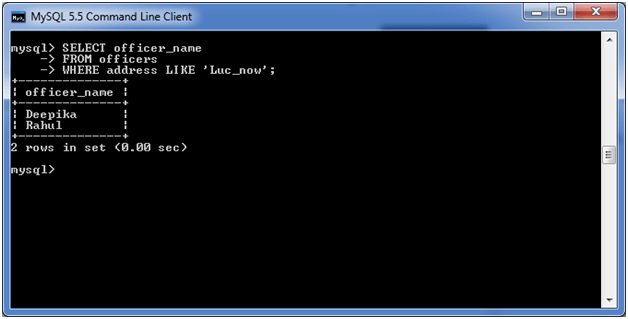
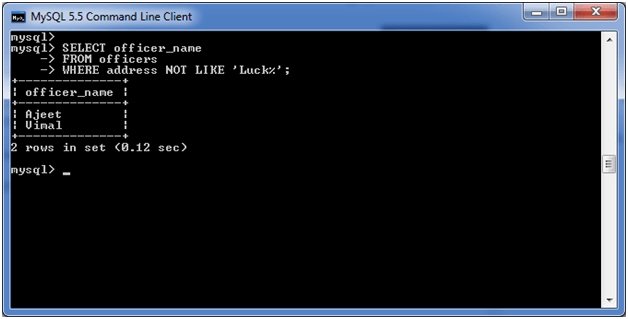
3) Using NOT Operator:
You can also use NOT operator with MySQL LIKE condition. This example shows the use of % wildcard with the NOT Operator.
Consider a table “officers” having the following data.
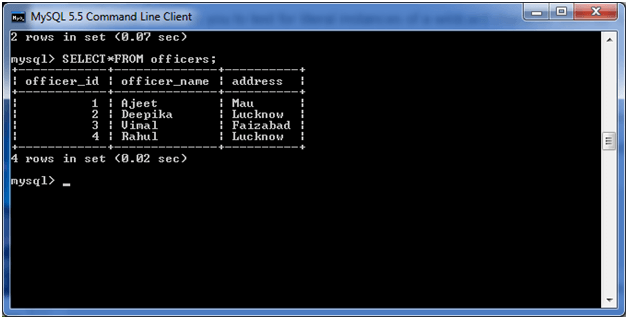
Execute the following query:
SELECT officer_name
FROM officers
WHERE address NOT LIKE 'Luck%'; Output:
Leave a Reply