A version is a specific form of something that varies from other forms of the same version. This article will explain the complete overview to find the SQL Server version running on your system.
We can get the SQL Server version in multiple ways, and some of them are listed below:
- Using a Query
- Using Console/Command Prompt
- Using SQL Server Management Studio
- Using PowerShell
- Using Log Files
- Using SQL Server Properties
Let us discuss each in detail.
Using a Query
It is the easiest way to see the SQL Server version installed on our system. We can use the @@VERSION function to get all of the SQL Server instance’s version details. This function returns a one-line string output containing all the relevant information about the SQL Server. It will display the following information in the output:
- SQL Server Version
- Processor Architecture
- SQL Server Build Date
- Copyright Statement
- SQL Server Edition
- Operating System Version
Now, we will execute the below query to see the current version of the SQL Server:
SELECT @@VERSION AS 'SQL Server Version' Here is the output:

The below table will explain this information in a meaningful form:
| SQL Server Version | Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (RTM) – 15.0.2000.5 |
| Processor Architecture | X64 |
| SQL Server Build Date | Sep 24 2019 13:48:23 |
| Copyright Statement | Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation |
| SQL Server Edition | Express Edition (64-bit) |
| Operating System Version | Windows 10 Enterprise 10.0 (Build 18362: ) |
Using Console/Command Prompt
Command prompt simulates the input field in a text-based user interface screen with the Windows GUI. It can be used to run commands and carry out advanced administrative tasks.
We can find the SQL Server version using console using the below steps:
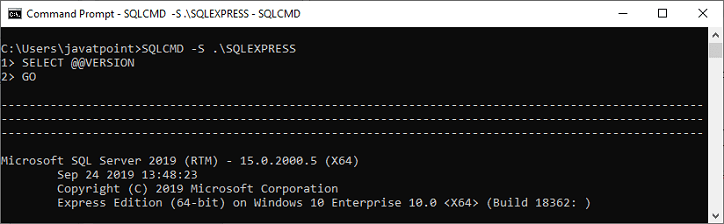
SQLCMD -S servername\instancename Here we need to change the name in place of servername and instancename.
The following image shows the SQL Server version on the cmd screen. We can repeat this process in other instances.
Using SQL Server Management Studio
SSMS is a valuable tool for managing the SQL Server installation. When we open SSMS for any SQL Server instance, we can see the product version appears under the Object Explorer tab between the parentheses. We can identify the SQL Server product version by this set of numbers. See the below image where the product version is shown on the red rectangular box:
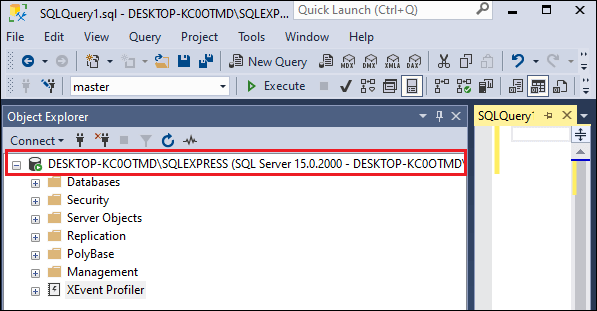
Let us convert this meaningless set of numbers into a meaningful product version. The product version is specified as 15.0.2000, which we convert into more meaningful and useful information. In this set of numbers, the first two digits (15) indicate the numeric definition of the SQL Server product name.
We can find the SQL Server version against the product name with the help of the following table quickly:
| SQL Server Product Name | SQL Server Product Version |
|---|---|
| SQL Server 2019 | 15.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2017 | 14.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2016 | 13.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2014 | 12.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2012 | 11.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2008 R2 | 10.5.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2008 | 10.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2005 | 9.0.xxxx.xx |
| SQL Server 2000 | 8.0.xxxx.xx |
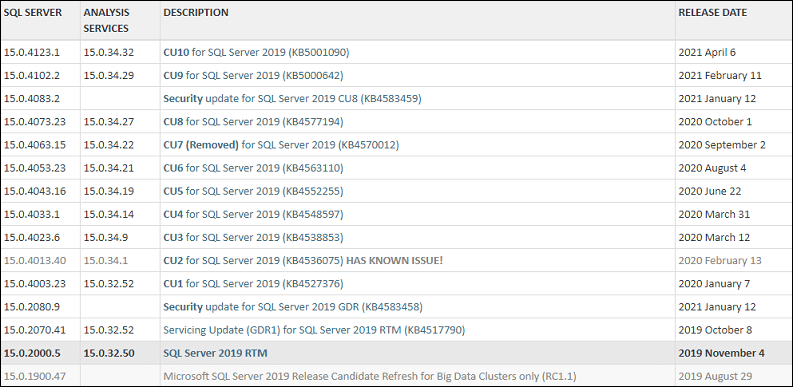
However, the first two digits provide the product name, and we can get more information about the SQL Server instances. The remaining numbers (0.2000) determine the service pack and cumulative upgrade levels details. We can get more details regarding the remaining numbers; we need to visit the BuildNumbers website:
Using PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful cross-platform tool for automation tasks made up of a command-line shell, a scripting language, and simplifying configuration. It can automate almost every Windows, Linux, and macOS activity, including Active Directory and Exchange. Microsoft has two modules of SQL Server PowerShell, but both are not installed with SSMS starting with version 17.0:
- SqlServer: newer, requires PowerShell 5.0
- SQLPS: no longer being updated
We can also find the installed SQL server version using PowerShell by entering the following command:
Invoke-SqlCmd -query "SELECT @@VERSION" -ServerInstance "localhost" Using Log Files
We can also find the SQL Server version in the SS error logs file. This file can be used to troubleshoot SQL Server issues because it records user-defined events as well as specific device events. It will also help us to get SQL Server version details. The first few lines of this file provide detailed information regarding the SQL Server’s version.
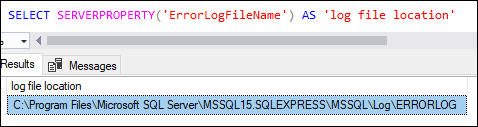
The error log is located in “Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.n\MSSQL\LOG” by default. However, we can also have an option SERVERPROPERTY function to get the location of the error log file. We can find the position of the error log file using the following query:
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('ErrorLogFileName') AS 'log file location' It will display the below output:
Now, we can open the error log file in the given location. Here we can see the detailed information about SQL Server build.
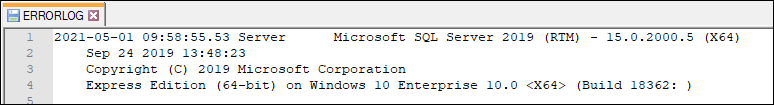
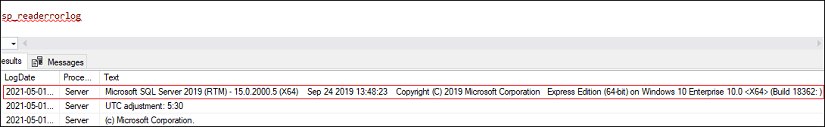
We can also read the error log by using the stored procedure sp_readerrorlog. The first line of its output shows the SQL Server instance details:
Using SQL Server Properties
We can also use the SQL Server properties method to get the SQL server version information. It is one of the easiest methods to get the SQL server version details.
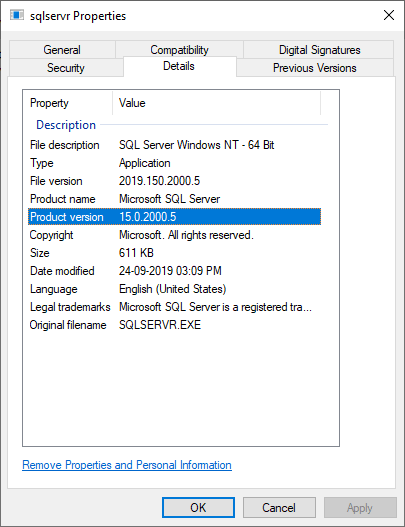
In this method, we need to navigate to the C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Binn. Now, search the sqlservr executable file, right-click on it to open the context menu, and select the Properties option. We will get the wizard where we will click the Details tab to see the product version and product name.
Conclusion
This article will explain various methods to check the SQL Server version and learned how to convert them into meaningful information.
Leave a Reply