In this section, we are going to learn the PostgreSQL insert command and examples, insert a date using the default keyword, and insert the data from one table to another in PostgreSQL pgAdmin and SQL shell (psql).
In PostgreSQL, the INSERT command is used to insert new rows into a table. We can insert a single row or multiple row values at a time into the particular table.
Syntax for PostgreSQL Insert command
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME
(column1,
column2,
column3, ……columnN)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ….. valueN); Inserting a single record using the default value keyword
If we insert a single record using the default values keyword, the INSERT command’s syntax is as follows:
INSERT INTO table
(column1, column2, ... )
DEFAULT VALUES; Inserting the multiple records using a sub-select
If we insert multiple records using the sub-select, the Insert command syntax is as follows:
INSERT INTO table_name
(column1, column2, ... )
SELECT expression1, expression2, ...
FROM source_table
[WHERE conditions]; The below table shows the Parameters or Arguments used in the insert table syntax:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Table_name | It is used to represent the existing table name. |
| column1, column2… columnN | These are the names of the columns in the table where we want to insert data. |
| WHERE conditions | It is an optional parameter and used in the third syntax. These are the conditions that must be occurred for the records to be inserted. |
| DEFAULT VALUES | All columns will be defined with their default values. And it is used in the second syntax. |
| source_table | It is used when we want to insert the data from another table. And it is used in the third syntax. |
| expression1 | DEFAULT, expression2 | DEFAULT | These are the values allocated to the columns in the table. If expression1 is specified, then column1 would be granted the value of expression1, column2 would be given the value of expression2, and so on. If DEFAULT is specified, the consistent column will be occupied with its default value. And it is used in the first syntax. |
Note
- We must offer each NOT NULL column value if we are inserting the records into a table using the PostgreSQL insert command.
- If the column allows NULL values, we can ignore a column from the PostgreSQL insert command.
Output
The following table shows the output messages and their meaning:
| Output message | Description |
|---|---|
| INSERT Oid 1 | If only one row was inserted and Oid is the numeric OID of the inserted row. |
| INSERT 0 # | This message will come if more than one row was inserted, and # is the number of rows inserted. |
PostgreSQL insert command
We can execute the PostgreSQL insert command in two ways:
- PostgreSQL Insert statement using UI (pgAdmin)
- PostgreSQL Insert statement using SQL shell
PostgreSQL Insert statement using UI
Let’s take an example to see how to insert values in a table. Here, we have a table named Student.
Example1: VALUES keyword
For creating a PostgreSQL INSERT command to list the values, we will use the VALUES keyword.
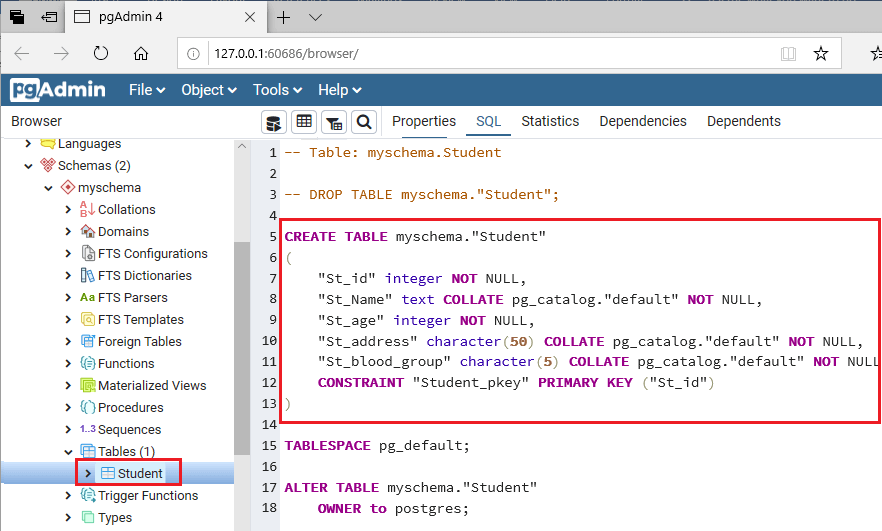
To insert values in the Student table, we are going to follow these below steps:
Step1
- Firstly, we will select Student table and then right-click on that, then select the Script option from the given list and click on the INSERT Script option from another list as we can see in the below screenshot:
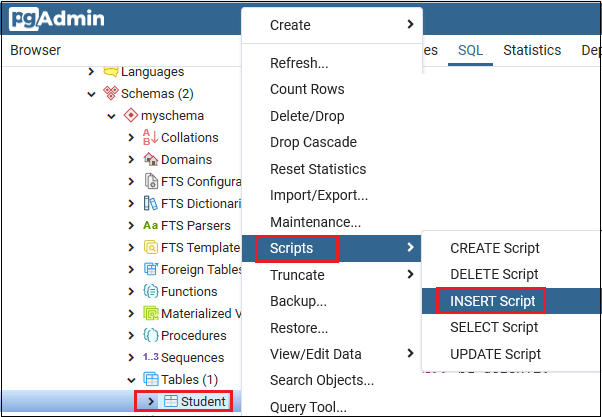
Step2
- Once we click on the Insert Script, the below window will appear on the screen:
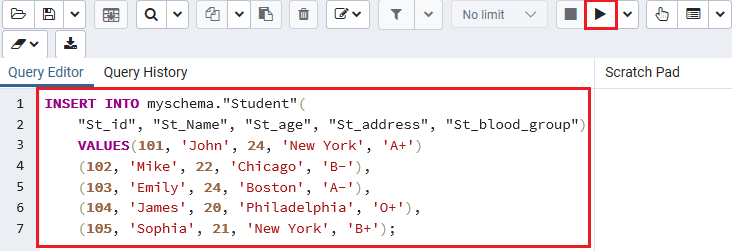
Step3
- Now, we insert the values in the place of ‘?’ then click on the execute/ refresh button for executing the particular command, and add the record into the Student table.
INSERT INTO myschema."Student"(
"St_id", "St_Name", "St_age", "St_address", "St_blood_group")
VALUES(101, 'John', 24, 'New York', 'A+')
(102, 'Mike', 22, 'Chicago', 'B-'),
(103, 'Emily', 24, 'Boston', 'A-'),
(104, 'James', 20, 'Philadelphia', 'O+'),
(105, 'Sophia', 21, 'New York', 'B+'); SQL Query in PgAdmin4
In the below screenshot, we can see the above command in pgAdmin4:
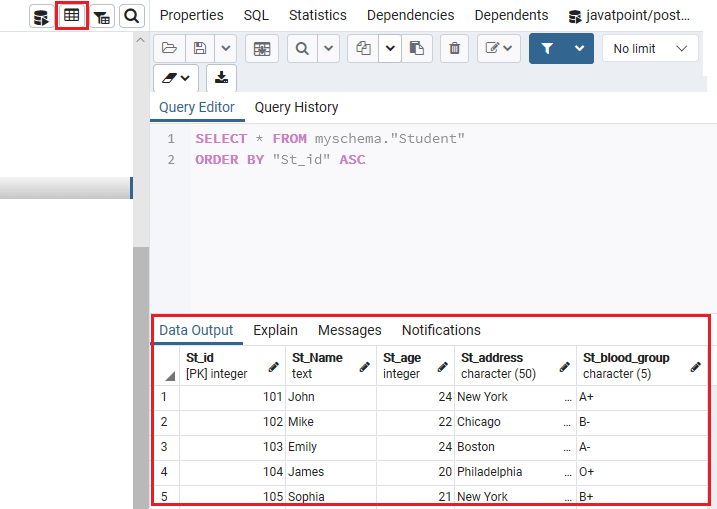
The table Structure/Output
After executing the Insert command, we can see the Student table’s output by clicking on the view table option as we can see in the below screenshot:
Example2
Firstly, we will create one new table for understanding the usage of the insert command in PostgreSQL.
Note: We can also refer to the below link to create a new table in PostgreSQL.
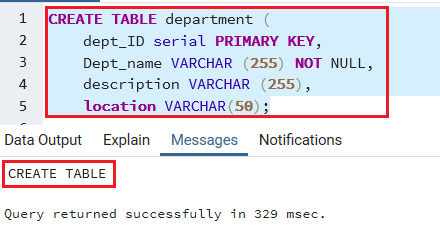
For now, we will create a department table with the help of the below command:
CREATE TABLE department (
dept_ID serial PRIMARY KEY,
Dept_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
description VARCHAR (255),
location VARCHAR(50)
); After executing the above command, we will get the below message that the department table has been created:
Example: Insert one-row value in a table
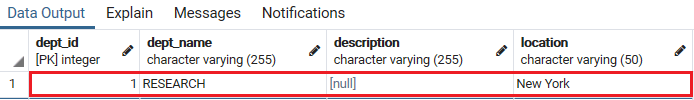
The below command is used to insert the dept_name, location value into the department table:
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, location)
VALUES ('RESEARCH', 'Newyork'); We can check the inserted row in the particular table using the SELECT command:
SELECT * FROM department; Output
Once we execute the above select command, we will get the below output:
If we want to insert character data, we must enclose it in single quotes (‘).
For example, ‘RESEARCH’.
PostgreSQL offers value for the serial column repeatedly; thus, it is not required to insert a value into the serial column.
Example: Insert the multiple rows using sub-select
Here, we will insert the various rows value using sub-select into the particular table.
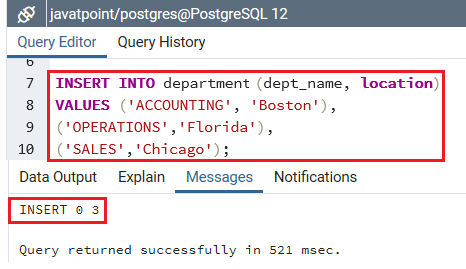
For example: In the below command, we will insert the multiple rows in dept_name, location columns of the department table:
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, location)
VALUES ('ACCOUNTING', 'Boston'),
('OPERATIONS','Florida'),
('SALES','Chicago');Once we implement the above command, we will get the below message that the three values have been inserted in the dept_name and the department table’s location columns:
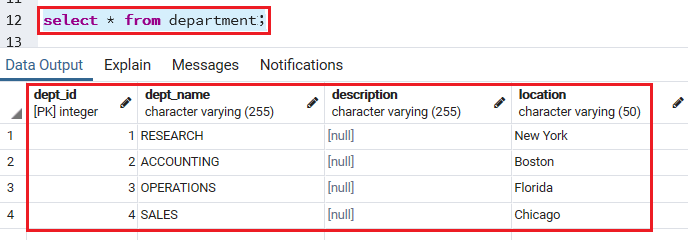
We can check the inserted row in the particular table with the help of SELECT command:
SELECT * FROM department; Output
Once we implemented the above select command, we will get the below output:
Example: Insert a date into a table using Default keyword
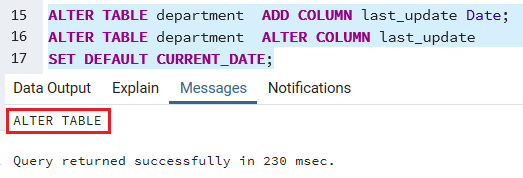
Firstly, we will add a new column named last_update into the department table and set its default value to current_date as we can see in the below command:
ALTER TABLE department ADD COLUMN last_update Date;
ALTER TABLE department ALTER COLUMN last_update
SET DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE; After executing the above command, the department table is altered, and the last_column has been created.
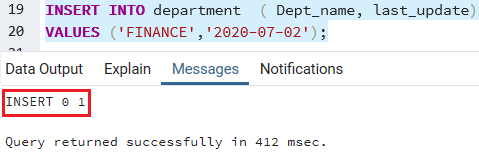
The below command is used to insert a new row to define the date into the department table.
Note: In PostgreSQL, the date format is YYYY-MM-DD.
INSERT INTO department ( Dept_name, last_update)
VALUES ('FINANCE','2020-07-02'); Output
After executing the above command, we will get the message window:
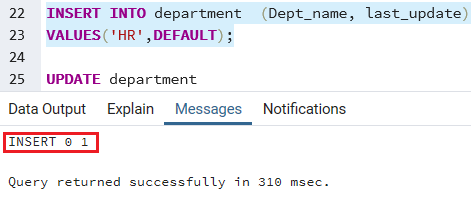
To set the default value for the date column or any other column, we can also use the DEFAULT keyword as we can see in the below command:
INSERT INTO department (Dept_name, last_update)
VALUES('HR',DEFAULT); Output
After performing the above command, we will get the below message window that the particular values have been inserted in the department table:
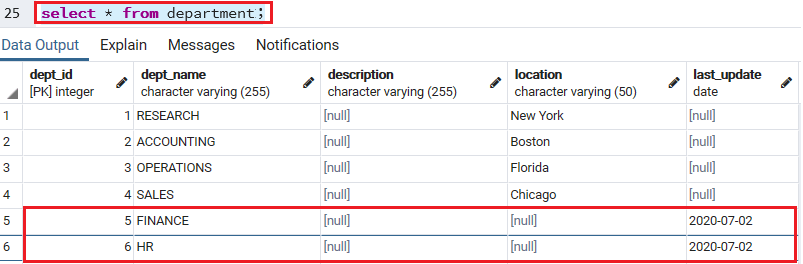
To check the inserted records in the department table, we will use the SELECT command:
Select * from department; Output
We will get the below result, after executing the above command:
Example: Insert data from another table
To insert data from another table, we will follow the below steps:
Step1
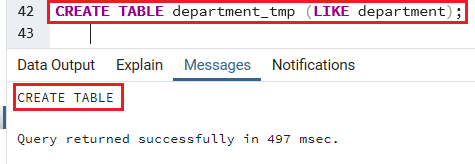
Firstly, we create another table called department_tmp, which has a similar table structure like the department table:
CREATE TABLE department_tmp (LIKE department); The department_tmp has been created after executing the above command:
Step2
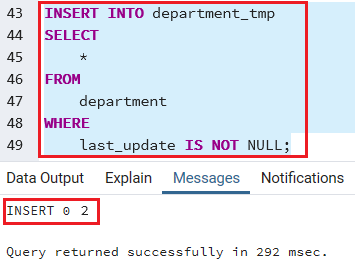
Once we create the table, we will insert the rows from the department table whose values of the date column are not NULL:
INSERT INTO department_tmp
SELECT *
FROM
department
WHERE
last_update IS NOT NULL; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message window, which displays that the particular values have been inserted successfully.
Step3
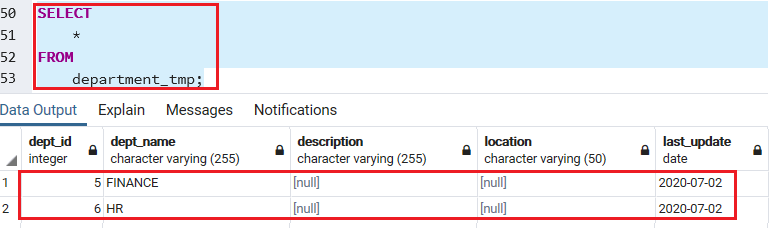
After that, we will check the insert operation using the SELECT command from the department_tmp table:
SELECT * FROM department_tmp; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below output:
If we want to get the last inserted dept_id from the department table, we will follow the below process:
Once we insert the new row in the insert command, we will use the RETURNING clause, a PostgreSQL extension to SQL.
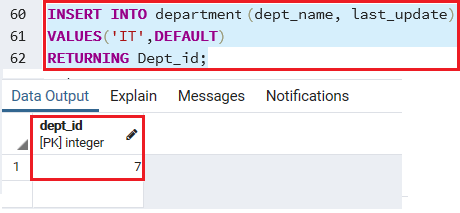
The following command inserts a new row into the department table and returns the last inserted Dept_id:
INSERT INTO department (dept_name, last_update)
VALUES('IT',DEFAULT)
RETURNING Dept_id;Output
Once we implemented the above command, we will get the Dept_id=7.
After that, we will use the Select command to check that the dept_id is correct or not.
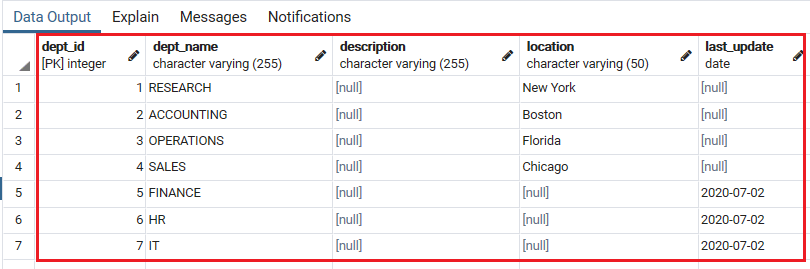
Select * from department; Output
Once we execute the Select command, we can see that the Once we created the customer table, we will insert a one-row into the Customer table with the help of below command:Dept_id matches the last inserted Dept_ id in the department table.
PostgreSQL Insert command Using psql
In SQL shell(psql), we will first create one table named Customer table in javatpoint database with the help of the below command:
CREATE TABLE Customer(
Cust_Id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
Cust_Name TEXT NOT NULL,
Cust_Address CHAR(30),
Cust_Age INT NOT NULL Unique
); Once we created the customer table, we will insert a one-row into the Customer table with the help of below command:
insert into customer (Cust_Id ,cust_name, Cust_address,Cust_age)
values(101, 'john', 'boston',22); After that, we will insert the multiple rows in the particular table, as we can see in the below command:
INSERT INTO Customer
(Cust_Id ,cust_name, Cust_address,Cust_age)
VALUES (102, 'mike', 'newyork',24),
(103,'emily', 'newyork',23),
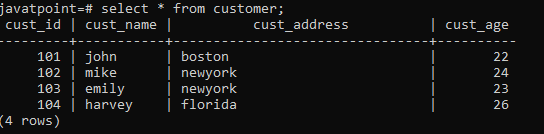
(104, 'harvey', 'florida',26); We will use the SELECT command to check whether the above values are inserted in the Customer table or not.
Select* from customer; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below output:
Leave a Reply