In this section, we are going to learn how to create a schema and create a table in schema commands in pgAdmin 4 and SQL shell(psql).
In PostgreSQL, the Schema is a namespace which provides various objects such as data types, indexes, tables, operators, views, sequence, and functions. And the create statement provides the exact object name, which helps us create the object in the existing schema.
Creating Schema in PostgreSQL
The CREATE SCHEMA statement is used to create a new schema into the existing database. This statement can contain subcommands for creating objects in the new schema. And the schema name should be different from the name of any current schema in the existing database.
In PostgreSQL, we can create the schema in two different ways:
- Create schema in pgAdmin 4
- Create schema in psql
Note: The CREATE SCHEMA command is used to create a schema, and it cannot be nested.
The syntax for creating a schema
CREATE SCHEMA schema_name;
Or
CREATE SCHEMA [IF NOT EXISTS] schema_name;We have the following parameters which are used in the above syntax:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Schema | Create schema is a keyword, which is used to create a new schema in the database. |
| Schema_Name | This parameter is used to describe the name of the schema, and the schema name should be exclusive in the existing database. |
| If not exists | This is an optional parameter, and it is used to create a new schema only if it does not occur. Or If we are trying to create a new schema without using the IF NOT EXISTS option, which is already present, it will produce an error. |
Note: To implement the create schema command, we should have the CREATE privileges in the existing database.
Creating Schema in pgAdmin 4 [Graphical user interface]
In this, we are going to create a schema in the latest version of pgAdmin. We need to follow the below steps to create a schema:
Step1
- Firstly, open pgAdmin in our local system and connect PostgreSQL to the localhost server.
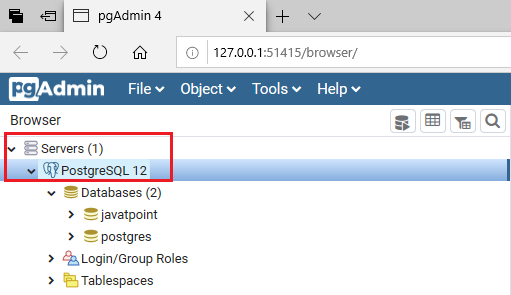
Step2
- After that, we will expand the databases by clicking on the down-arrow icon, as shown in the below screenshot:
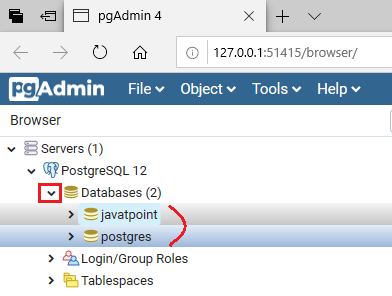
- In the above image, we can see that there are two databases available in PostgreSQL. And here, we are taking the first database, which is javatpoint.
Step3
- Now, we will expand the database javatpoint.
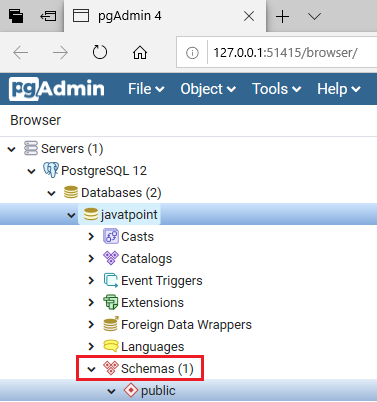
Step4
- Once we expand the javatpoint database, we can see the Schemas.
- After that, for creating a schema, we will right-click on the Schemas option, and then select Create, and then click on schema option from the list.
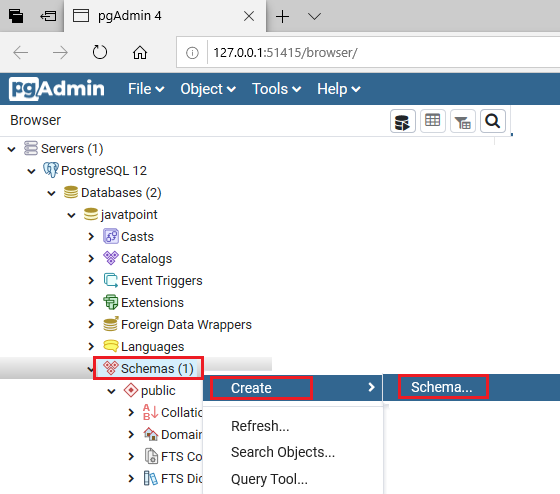
Step5
- Once we clicked on the schema, the Create-schema window will appear on the screen where we will provide all the necessary details like Name, etc., and click on the Save
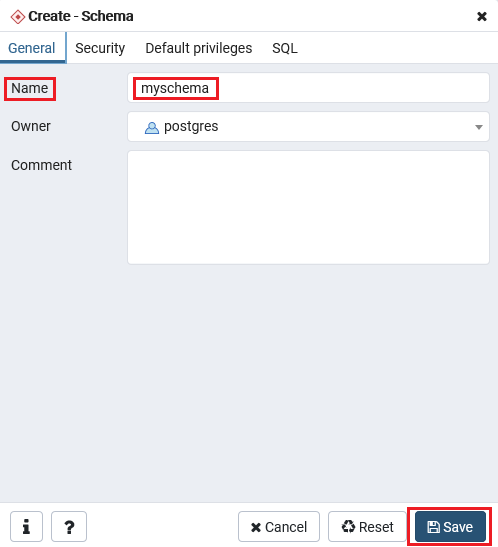
Step6
- The myschema has been created once we clicked on the Save button, as shown in the below screenshot:
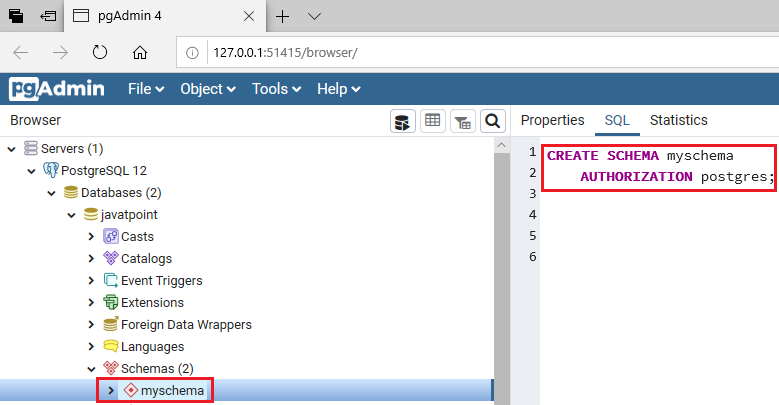
Creating a schema in psql
- Firstly, we will connect to the javatpoint database, and create a new schema as Jtp with the help of below command:
javatpoint=# create schema jtp;
CREATE SCHEMA 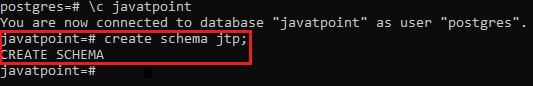
- The message CREATE SCHEMA indicates that the schema is created successfully.
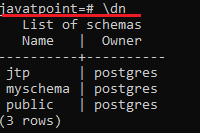
- To check whether the schema is created or not, we can execute the below command:
Javatpoint=#\dn - After executing the above command, we can see the list of schema in the below screenshot:
PostgreSQL Create Table in Schema
Here we are going to create a table in the particular schema (which we created earlier in this section). In PostgreSQL, we can create a table in the schema in two different ways:
- Create a table in pgAdmin schema
- Create a table in psql schema
Create a table in pgAdmin schema
Once we are done creating the schema in pgAdmin, we are going to create a table in the particular schema. And for this we are going to follow the below steps:
Step1
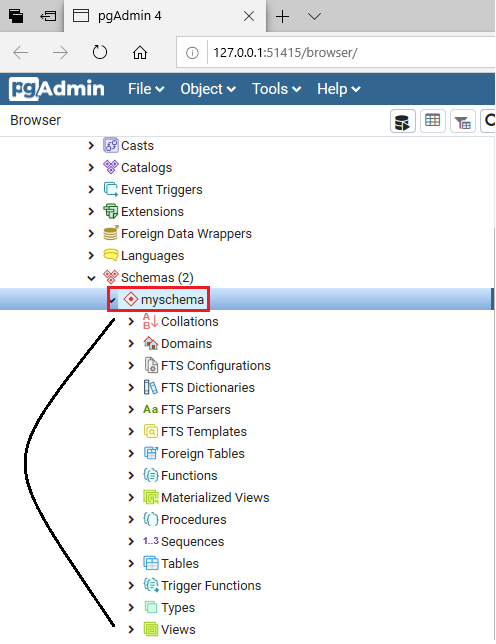
- Firstly, we are expanding the newly created schema myschema, and we can see the myschema contains the following:
- Collations
- Tables
- Sequences
- Functions
- Procedure
- Types
- View and so on.
Step2
- Now, we will right-click on the Tables option under the myschema, and where we will select the Create option from the given drop-down and then click on the Table as we can see in the below image:
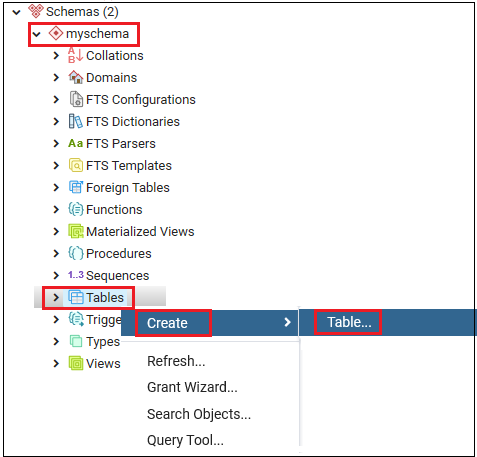
Step3
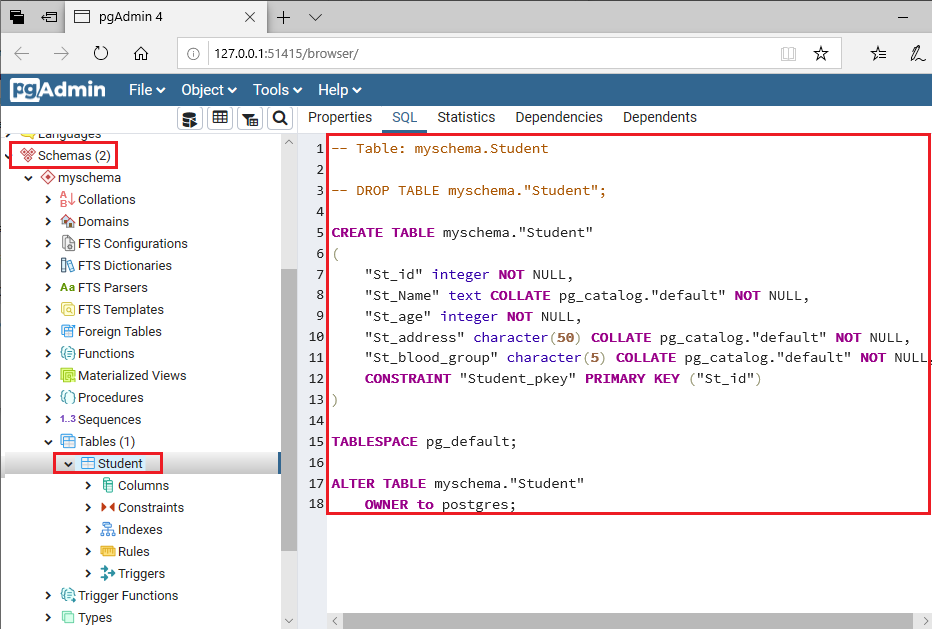
- Once we clicked on the table option, the Create-Table window will appear on the screen where we will enter all the necessary details like Table name. In our case, we will create a table called Student.
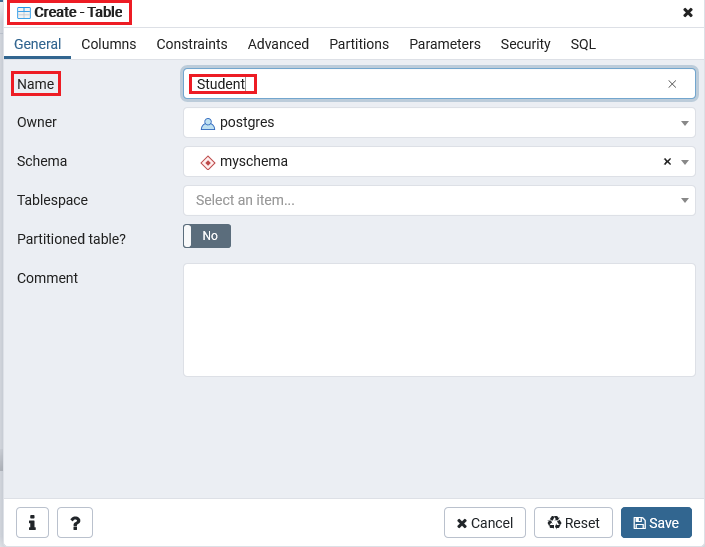
Step4
- After that, we will move to the Column tab in the same window then click on the + sign to add columns in a particular table.
- And we can select the Data types from the given drop-down list as well as we can change the columns Not-null preference and also set the Primary key.
- And then click on Save to complete the process of creating a table as we can see in the below screenshot:
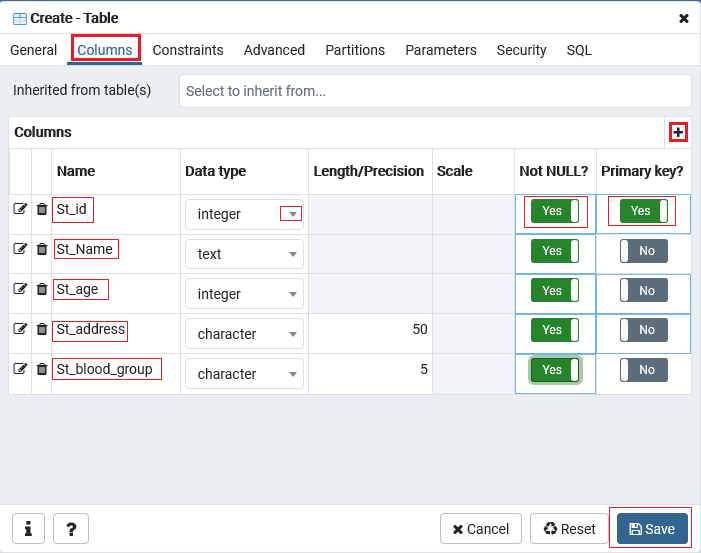
- And we can see that the Student table is created under the Table
Create a table in the psql schema
Now, we will create a table in the psql schema, which we created above. But first, we will see the syntax of creating a table in psql schema.
The syntax to Create Table in Schema
The general syntax, for creating a table in the schema is as follows:
CREATE TABLE Schema_name.Table_name (
); The following parameters are used in the above syntax:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Create table | Create table is a keyword, which is used to create a table in the existing schema. |
| Schema_name | It is used to specify the current schema name. |
| Table_name | It is used to describe the name of the table, and the table name should be unique in the existing schema. |
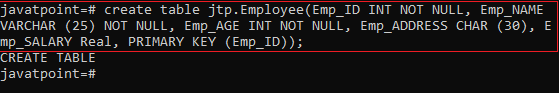
- The below command is used to create a table in the psql schema:
javatpoint=# create table jtp.Employee(
Emp_ID INT NOT NULL,
Emp_NAME VARCHAR (25) NOT NULL,
Emp_AGE INT NOT NULL,
Emp_ADDRESS CHAR (30),
Emp_SALARY Real,
PRIMARY KEY (Emp_ID)
); 
- The above command will create an empty table. And we can check the created table with the help of below command:
javatpoint=# select * from jtp.Employee; Output
The following screenshot will display the result of the above-created table:
Leave a Reply