In SQL Server, foreign key is used to enforce referential integrity within your SQL Server database. It specifies that a value in one table must also appear in another table.
The referenced table is called parent table while the table having foreign key is called child table. The foreign key in the child table will generally reference a primary key in the parent table.
A foreign key can be created using either a CREATE TABLE statement or an ALTER TABLE statement.
Create a Foreign Key using CREATE TABLE statement
CREATE TABLE child_table
(
column1 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
...
CONSTRAINT fk_name
FOREIGN KEY (child_col1, child_col2, ... child_col_n)
REFERENCES parent_table (parent_col1, parent_col2, ... parent_col_n)
[ON DELETE {NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT} ]
[ON UPDATE {NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT} ]
);Parameter Explanation
child_table: It specifies the name of the child table that you want to create.
column1, column2: It specifies the columns that you want to create in the table. Each column must have a datatype. The column should either be defined as NULL or NOT NULL and if this value is left blank, the database assumes NULL as the default.
fk_name: It specifies the name of the foreign key constraint that you want to create.
child_col1, child_col2, … child_col_n: It specifies columns in child_table that will reference a primary key in the parent_table.
parent_table: It specifies the name of the parent table whose primary key will be used in the child_table.
parent_col1, parent_col2, … parent_col3: It specifies columns that make up the primary key in the parent_table. The foreign key will enforce a link between this data and the child_col1, child_col2, … child_col_n columns in the child_table.
Example:
Let’s create two table “products” and “inventory” where primary key of products table is “product_id” which is foreign key in “inventory” table.
CREATE TABLE products
( product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
category VARCHAR(25)
);
CREATE TABLE inventory
( inventory_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_id INT NOT NULL,
quantity INT,
min_level INT,
max_level INT,
CONSTRAINT fk_inv_product_id
FOREIGN KEY (product_id)
REFERENCES products (product_id)
);Output:
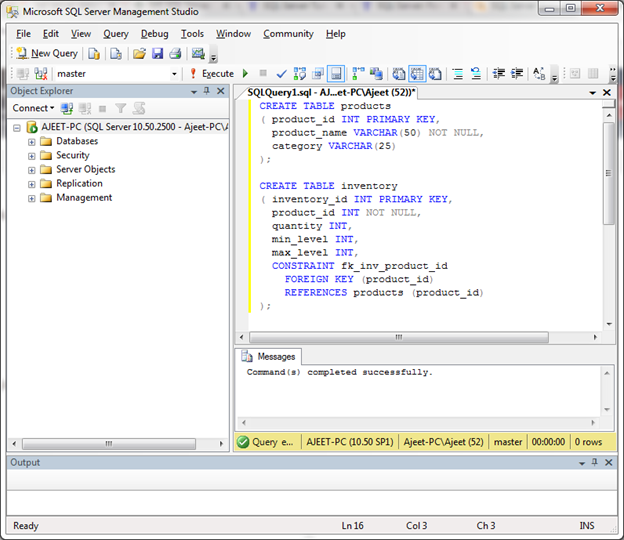
The foreign key constraint in “inventory” table is fk_inv_product_id. It will establish a relationship between the product_id column in the inventory table and the product_id column in the products table.
You can now check the both tables.
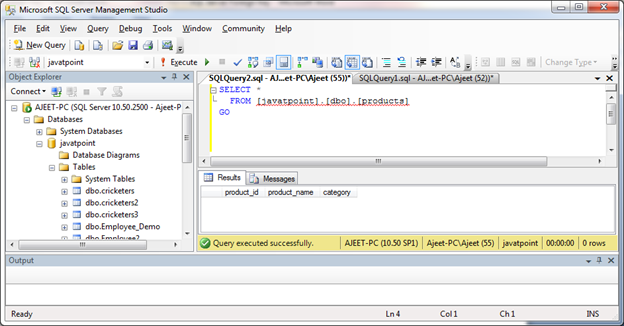
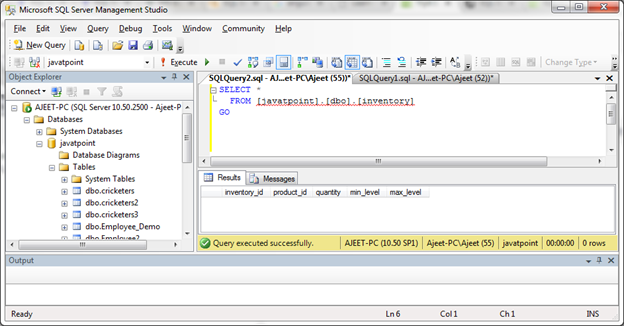
Create foreign key with more than one field
In the above example, we see how to create a foreign key having one column. Let’s create foreign key having more than one field.
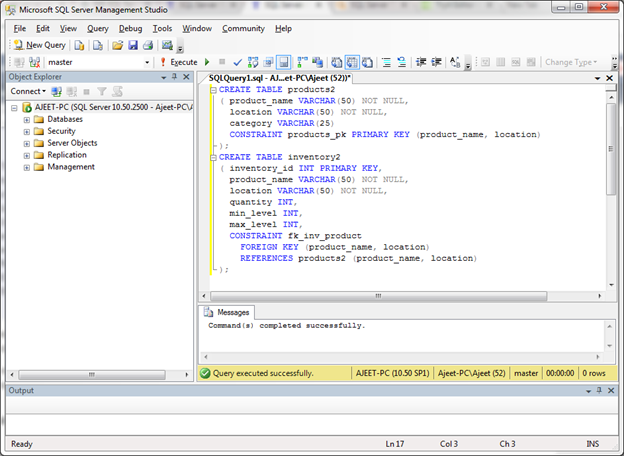
Let’s create two table “products2” and “inventory2”. In this example, “products2” table has a primary key that contains both the product_name and location columns. Therefore, the second table and foreign key must also reference these two columns.
So in this example, our foreign key called fk_inv_product references the products table based on two fields: the product_name and location fields.
CREATE TABLE products2
( product_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
location VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
category VARCHAR(25)
CONSTRAINT products_pk PRIMARY KEY (product_name, location)
);
CREATE TABLE inventory2
( inventory_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
location VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
quantity INT,
min_level INT,
max_level INT,
CONSTRAINT fk_inv_product
FOREIGN KEY (product_name, location)
REFERENCES products2 (product_name, location)
);Output:
Leave a Reply