A view is a virtual table created according to the result set of an SQL statement.
A view contains rows and columns, just like a real table. The columns in the view are the columns from one or more real tables in the database. SQL functions, WHERE, and JOIN statements can also be added to the view.
There are two ways to create a view in SQL Server:
- By using SQL Server management studio UI.
- By using SQL Server query statement.
By using SQL Server management studio UI
Open SQL Server Management Studio.
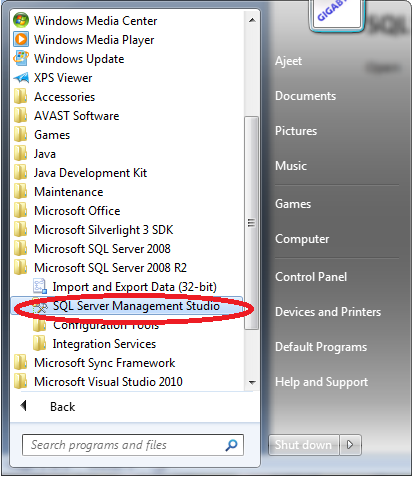
Here you see view. Go to view and click right.
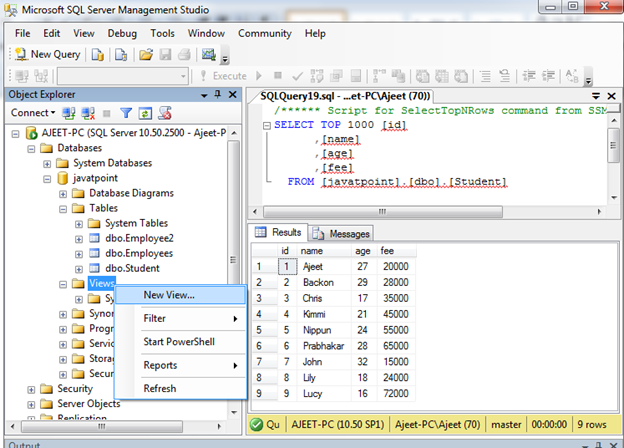
Now you will see a page like this. Choose a table on which you want to create a view. Here we select “Student” table.
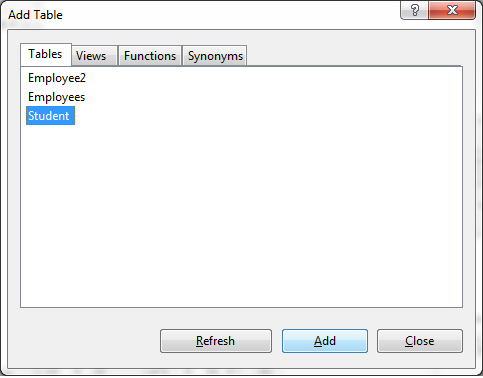
Click on the add button.
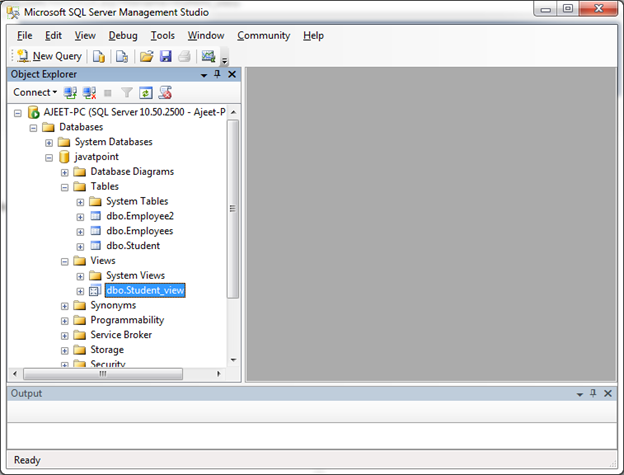
A view is created.
By using SQL Server query statement.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;SQL Create VIEW Example
Let’s create a view named “Student_name” which contains all data from table “Student” where id is >3.
CREATE VIEW [Student_view] AS
SELECT id, name, age
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Student]
WHERE id > 3;Output:

View is created successfully.
You can verify that created view:
SELECT * FROM [Student_view]; Output:
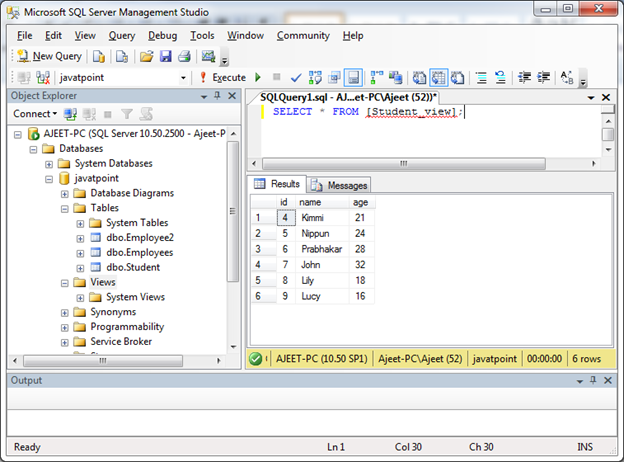
Update a View
You can update a view by using ALTER VIEW statement.
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;Now add a column “fee” to the created view “Student_view” from the table “Student”. Use the following statement:
ALTER VIEW [Student_view] AS
SELECT id, name, age, fee
FROM [javatpoint].[dbo].[Student]
WHERE id > 3;Output:
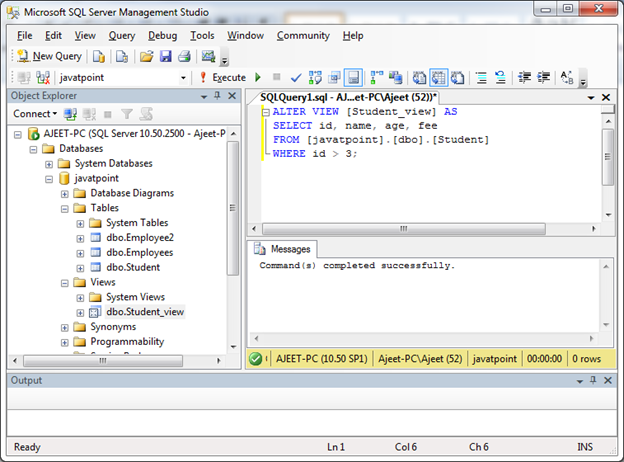
You can see that view is updated successfully. Verify it by using SELECT statement:
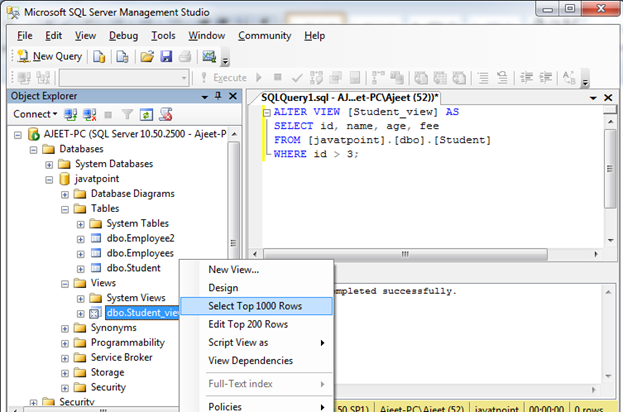
Output:
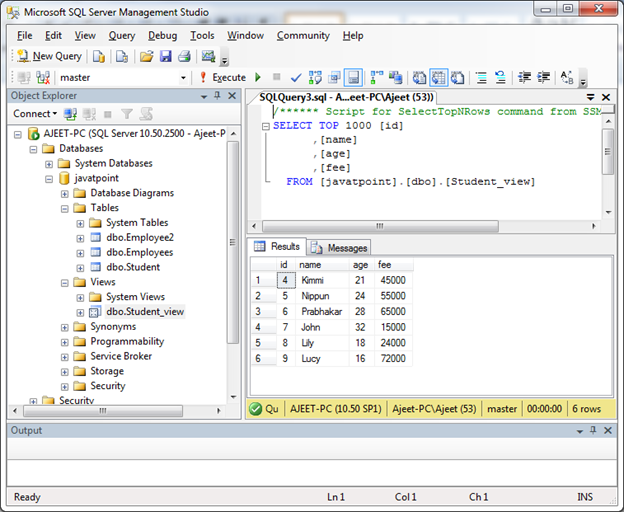
SQL Server DROP a View
DROP VIEW command is used to delete a view.
DROP VIEW view_name; Example:
Let’s delete the view “Student_view”.
DROP VIEW [Student_view]; Output:
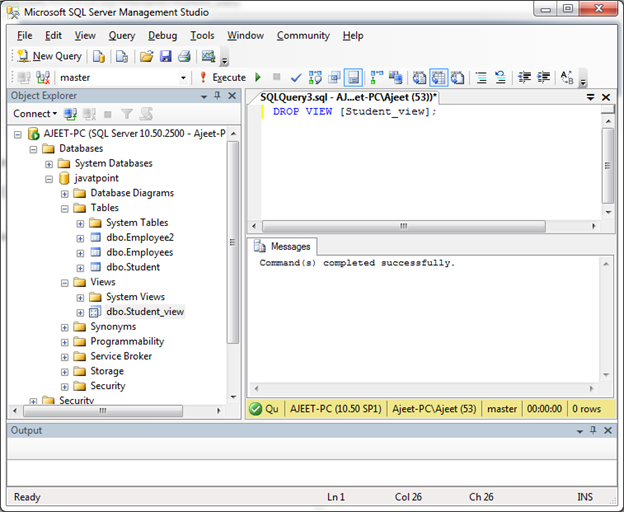
Now you can see that view is deleted.
Leave a Reply