To use SQLite with java programs, you must have SQLite JDBC Driver and Java set up on the system. Follow the steps given below:
- Download latest version of sqlite-jdbc-(VERSION).jar from sqlite-jdbc repository.
- Add the downloaded jar file to your class path.
- You can now connect to the SQLite database using java.
Connect to SQLite Database
Use the following code to connect to SQLite database using Java programming language:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Connect {
/**
* Connect to a sample database
*/
public static void connect() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
// db parameters
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C:/sqlite/JTP.db";
// create a connection to the database
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
System.out.println("Connection to SQLite has been established.");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
connect();
}
}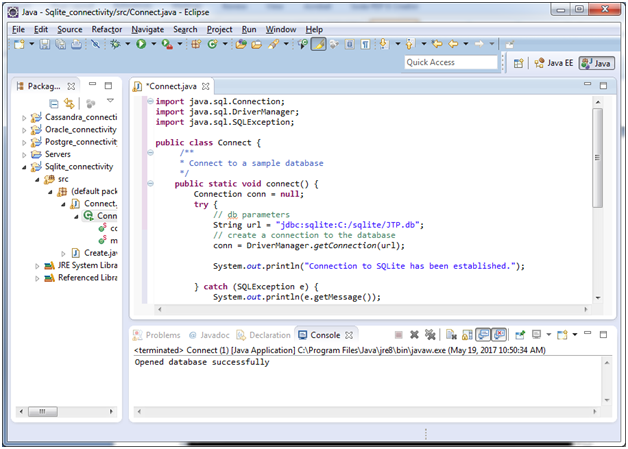
It is connected with your already created database JTP.db.
Create Database using java
You can also create a new database in SQLite using java programming language. Let’s create a database named “SSSIT.db”. Create a public class “Create” and use the following code:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Create {
public static void createNewDatabase(String fileName) {
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C:/sqlite/" + fileName;
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
if (conn != null) {
DatabaseMetaData meta = conn.getMetaData();
System.out.println("The driver name is " + meta.getDriverName());
System.out.println("A new database has been created.");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
createNewDatabase("SSSIT.db");
}
} 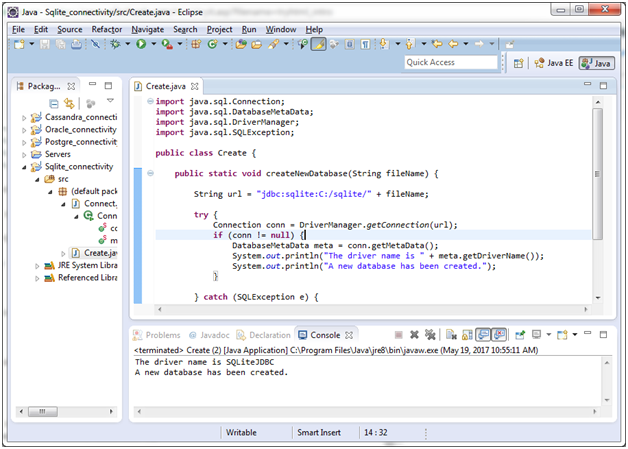
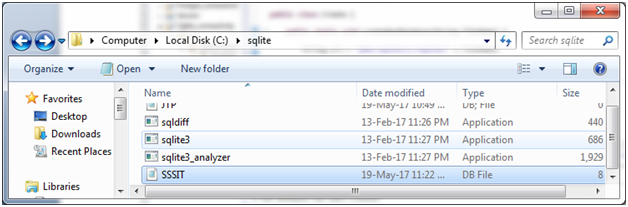
A new database named “SSSIT.db” is created now. You can see it where you have installed sqlite.
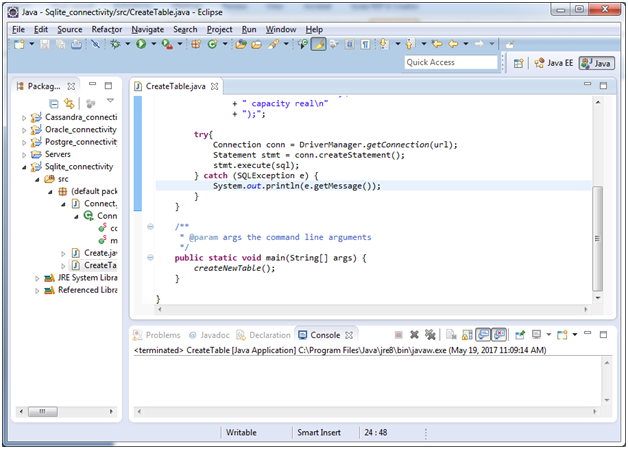
Create a table using java
Let’s create a table named “employees” having columns “name” and “capacity”. Create a class name “CreateTable”, having the following code:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class CreateTable {
public static void createNewTable() {
// SQLite connection string
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C://sqlite/SSSIT.db";
// SQL statement for creating a new table
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employees (\n"
+ " id integer PRIMARY KEY,\n"
+ " name text NOT NULL,\n"
+ " capacity real\n"
+ ");";
try{
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.execute(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
createNewTable();
}
} It will create a table “employees” within the SSSIT.db database.
Insert Record in the table
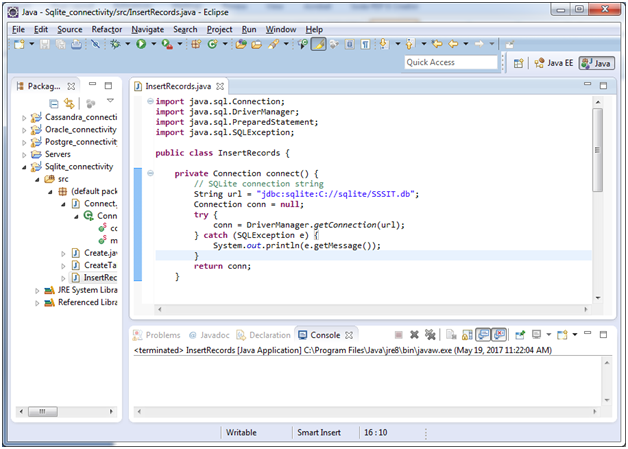
After the creation of the table, use the following code to insert some records in the table. Create a new class “InsertRecords”, having the following code:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class InsertRecords {
private Connection connect() {
// SQLite connection string
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C://sqlite/SSSIT.db";
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return conn;
}
public void insert(String name, double capacity) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(name, capacity) VALUES(?,?)";
try{
Connection conn = this.connect();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, name);
pstmt.setDouble(2, capacity);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InsertRecords app = new InsertRecords();
// insert three new rows
app.insert("Aryan", 30000);
app.insert("Robert", 40000);
app.insert("Jerry", 50000);
}
} 
Now record is inserted in the table. You can check it out by using the SELECT command:
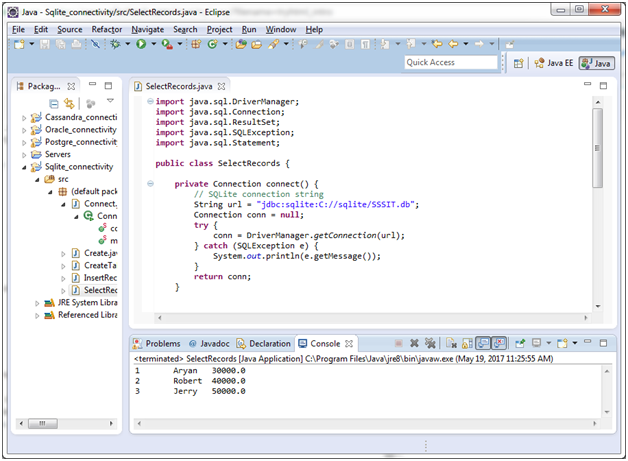
Select Records
To select records from the table, use the following code. Create a new class “SelectRecords”, having the following data.
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class SelectRecords {
private Connection connect() {
// SQLite connection string
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C://sqlite/SSSIT.db";
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return conn;
}
public void selectAll(){
String sql = "SELECT * FROM employees";
try {
Connection conn = this.connect();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// loop through the result set
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id") + "\t" +
rs.getString("name") + "\t" +
rs.getDouble("capacity"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SelectRecords app = new SelectRecords();
app.selectAll();
}
} Output:
You can see that it displays all the records we inserted once.
Note: By using the same procedure, you can update and delete the table and database.
Leave a Reply