In this section, we are going to discuss how we can drop the columns with the help of the ALTER TABLE command.
PostgreSQL DROP COLUMN Command
We will use the DROP COLUMN condition in the ALTER TABLE command for dropping a column of a table:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name;PostgreSQL will automatically delete all of its constraints and indexes, including the column while deleting a column from a table, and every drop column condition is separated by a comma (,).
We cannot delete those columns where the other objects depend on them and also used in other database objects like triggers, views, stored procedures, etc.
So, for removing those columns and all its connected objects, we will use the CASCADE option in the drop column command as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name CASCADE;If we want to delete a non-existing column, PostgreSQL will raise an issue. We will add the IF EXISTS condition in the drop column command to get over with this error as we can see in the below command:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN IF EXISTS column_name;In the above command, if we delete a column, which does not exist, PostgreSQL will raise a notice rather than an error.
We will use the below command if we need to remove the various columns of a table in a single command:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name_1,
DROP COLUMN column_name_2;Examples of PostgreSQL DROP COLUMN Command
Let us see some examples to understand the working of the ALTER TABLE DROP COLUMN command.
So, we will create three different tables, such as Product, Categories, and Brand.
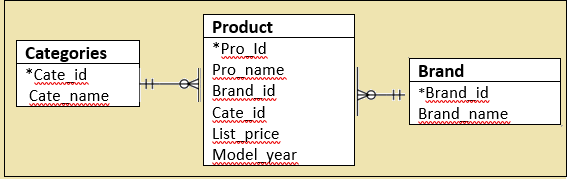
In the above diagram, each Product contains only one brand, and each brand can have several products. Each product is assigned to a category, and each category can have various products.
The following commands are used to create the three tables (Categories, Product, and Brand):
Creating the Categories table with the help of below command:
CREATE TABLE Categories (
Cate_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Cate_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
); Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message; the Categories table has been created.
Creating the Product table using the following statement:
CREATE TABLE Product (
Pro_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Pro_name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
Brand_id INT NOT NULL,
Cate_id INT NOT NULL,
List_price DECIMAL NOT NULL,
Model_year SMALLINT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (Cate_id) REFERENCES Categories (Cate_id),
FOREIGN KEY (Brand_id) REFERENCES Brand (Brand_id)
); Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message; the Product table has been created.
Creating the Brand table using the following command:
CREATE TABLE Brand (
Brand_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Brand_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
); Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message; the Brand table has been created.
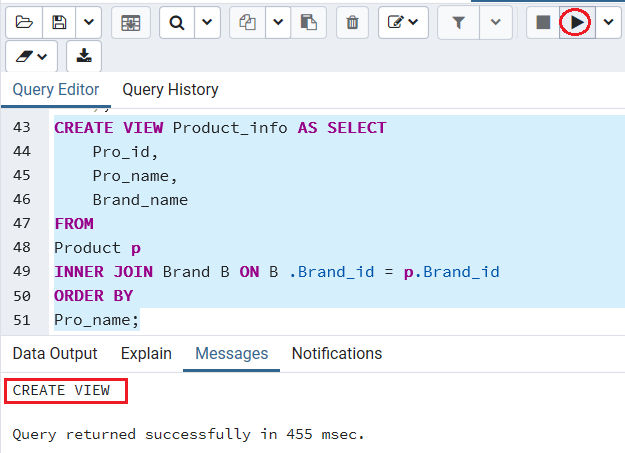
Besides, we create a view based on the Product and Brand tables as follows:
CREATE VIEW Product_info AS SELECT
Pro_id,
Pro_name,
Brand_name
FROM
Product p
INNER JOIN Brand B ON B .Brand_id = p.Brand_id
ORDER BY
Pro_name; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message; the Product_info view has been created.
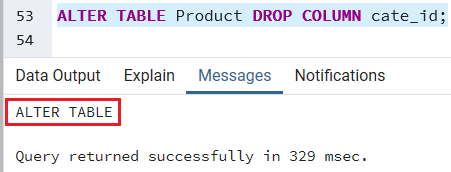
We will use the following command if we want to delete the cate_id column of the Product table:
ALTER TABLE Product DROP COLUMN cate_id; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message; the cate_id column dropped from the Product table.
If we want to see the table in psql, we will use the below command
Javatpoint=# \d Product; 
As we can see in the above screenshot, the above command deletes the Cate_id column and includes the Cate_id column into the foreign key constraint.
Now we will try to drop the Brand_id column from the Product table.
ALTER TABLE Product DROP COLUMN Brand_id; Once we execute the above command, PostgreSQL will raise the below error:
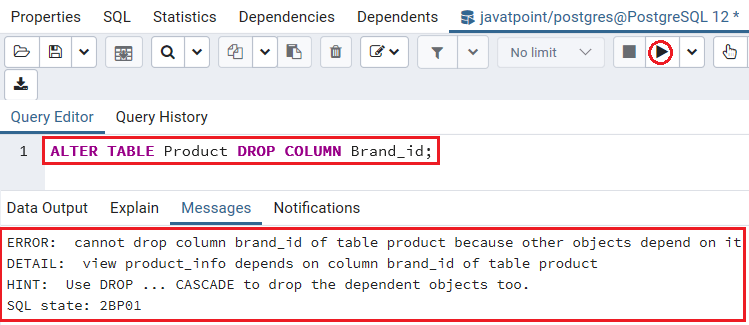
It stated that the product_info view is using the column Brand_id of the Product table.
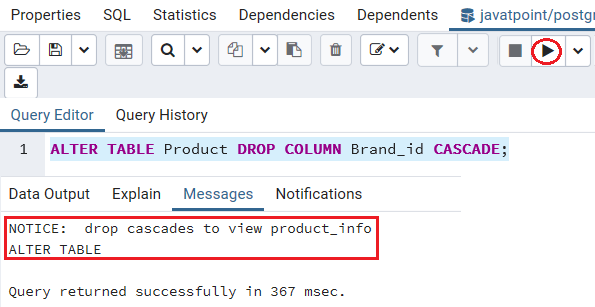
So, we will use the cascade option to delete both the Brand_id column and Product_info view with the below command’s help:
ALTER TABLE Product DROP COLUMN Brand_id CASCADE; Once we implement the above command, it will raise the below notice and drop the particular column.
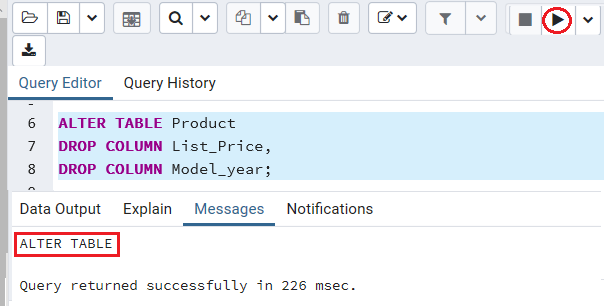
Here, we will drop both the list_price and Model_year columns in a single command, and we need to use the multiple DROP COLUMN conditions as we did below:
ALTER TABLE Product
DROP COLUMN List_Price,
DROP COLUMN Model_year; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below message window: The List_price and Model_year columns have been dropped from the Product table.
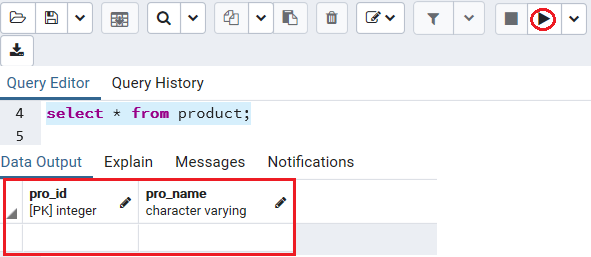
If we want to see the above operations are working fine or not, we will use the Select command:
Select * from Product ; Output
After executing the above command, we will get the below output:
Leave a Reply