Many times developers ask that is it possible to insert multiple rows into a single table in a single statement. Currently, developers have to write multiple insert statements when they insert values in a table. It is not only boring but also time-consuming.
Let us see few practical examples to understand this concept more clearly. We will use the MySQL database for writing all the queries.
Example 1:
To create a table in the database, first, we need to select the database in which we want to create a table.
mysql> USE dbs; Then we will write a query to create a table named student in the selected database ‘dbs’.
mysql> CREATE TABLE student(ID INT, Name VARCHAR(20), Percentage INT, Location VARCHAR(20), DateOfBirth DATE); 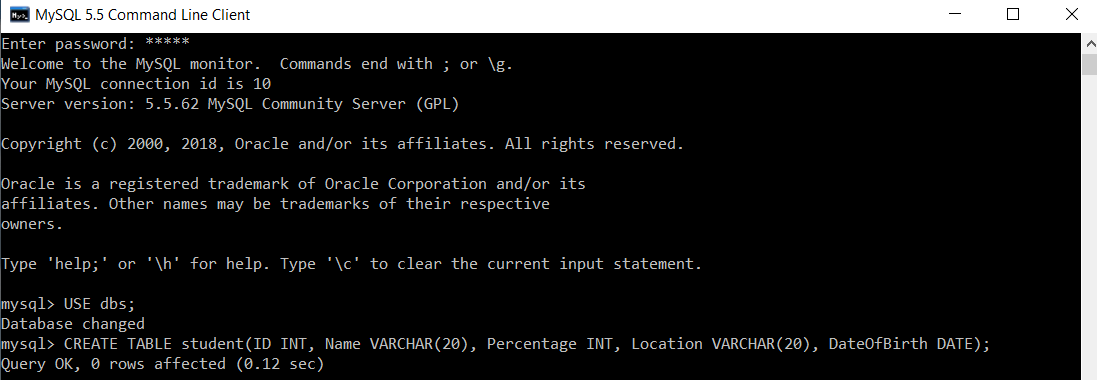
The student table is created successfully.
Now, we will write a single query to insert multiple records in the student table:
mysql> INSERT INTO student(ID, Name, Percentage, Location, DateOfBirth) VALUES(1, "Manthan Koli", 79, "Delhi", "2003-08-20"), (2, "Dev Dixit", 75, "Pune", "1999-06-17"), (3, "Aakash Deshmukh", 87, "Mumbai", "1997-09-12"), (4, "Aaryan Jaiswal", 90, "Chennai", "2005-10-02"), (5, "Rahul Khanna", 92, "Ambala", "1996-03-04"), (6, "Pankaj Deshmukh", 67, "Kanpur", "2000-02-02"), (7, "Gaurav Kumar", 84, "Chandigarh", "1998-07-06"), (8, "Sanket Jain", 61, "Shimla", "1990-09-08"), (9, "Sahil Wagh", 90, "Kolkata", "1968-04-03"), (10, "Saurabh Singh", 54, "Kashmir", "1989-01-06"); 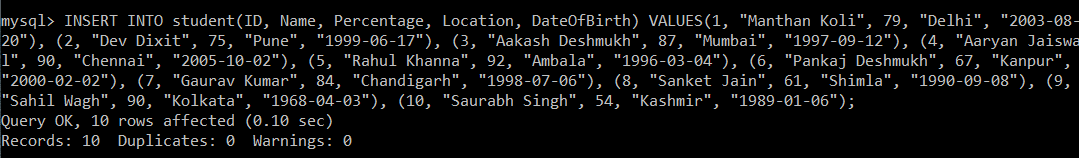
To verify that multiple records are inserted in the student table, we will execute the SELECT query.
mysql> SELECT *FROM student; | ID | Name | Percentage | Location | DateOfBirth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manthan Koli | 79 | Delhi | 2003-08-20 |
| 2 | Dev Dixit | 75 | Pune | 1999-06-17 |
| 3 | Aakash Deshmukh | 87 | Mumbai | 1997-09-12 |
| 4 | Aaryan Jaiswal | 90 | Chennai | 2005-10-02 |
| 5 | Rahul Khanna | 92 | Ambala | 1996-03-04 |
| 6 | Pankaj Deshmukh | 67 | Kanpur | 2000-02-02 |
| 7 | Gaurav Kumar | 84 | Chandigarh | 1998-07-06 |
| 8 | Sanket Jain | 61 | Shimla | 1990-09-08 |
| 9 | Sahil Wagh | 90 | Kolkata | 1968-04-03 |
| 10 | Saurabh Singh | 54 | Kashmir | 1989-01-06 |
The results show that all ten records are inserted successfully using a single query.
Example 2:
To create a table in the database, first, we need to select the database in which we want to create a table.
mysql> USE dbs; Then we will write a query to create a table named items_tbl in the selected database ‘dbs’.
mysql> CREATE TABLE items_tbl(ID INT, Item_Name VARCHAR(20), Item_Quantity INT, Item_Price INT, Purchase_Date DATE); 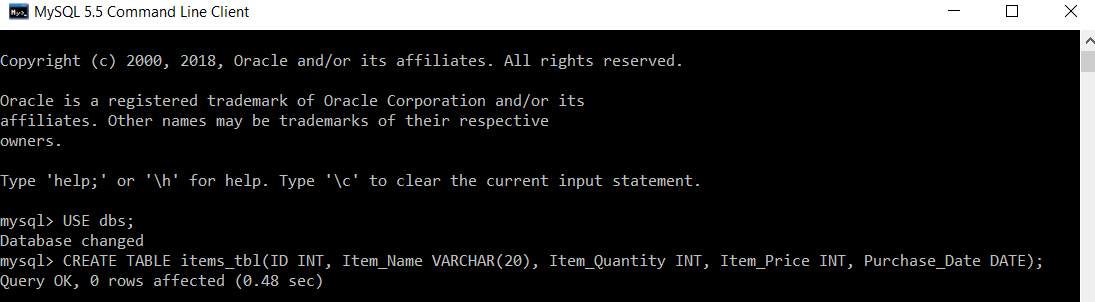
The table named items_tbl is created successfully.
Now, we will write a single query to insert multiple records in the items_tbl table:
mysql> INSERT INTO items_tbl(ID, Item_Name, Item_Quantity, Item_Price, Purchase_Date) VALUES(1, "Soap", 5, 200, "2021-07-08"), (2, "Toothpaste", 2, 80, "2021-07-10"), (3, "Pen", 10, 50, "2021-07-12"), (4, "Bottle", 1, 250, "2021-07-13"), (5, "Brush", 3, 90, "2021-07-15"), (6, "Notebooks", 10, 1000, "2021-07-26"), (7, "Handkerchief", 3, 100, "2021-07-28"), (8, "Chips Packet", 5, 50, "2021-07-30"), (9, "Marker", 2, 30, "2021-08-13"), (10, "Scissors", 1, 60, "2021-08-13"); 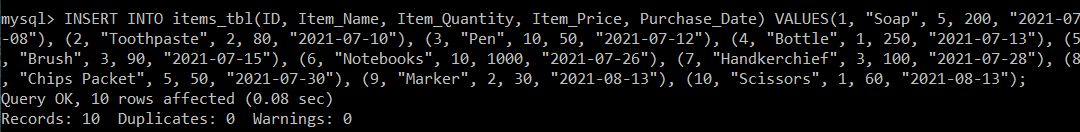
To verify that multiple records are inserted in the items_tbl table, we will execute the SELECT query.
mysql> SELECT *FROM items_tbl; | ID | Item_Name | Item_Quantity | Item_Price | Purchase_Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soap | 5 | 200 | 2021-07-08 |
| 2 | Toothpaste | 2 | 80 | 2021-07-10 |
| 3 | Pen | 10 | 50 | 2021-07-12 |
| 4 | Bottle | 1 | 250 | 2021-07-13 |
| 5 | Brush | 3 | 90 | 2021-07-15 |
| 6 | Notebooks | 10 | 1000 | 2021-07-26 |
| 7 | Handkerchief | 3 | 100 | 2021-07-28 |
| 8 | Chips Packet | 5 | 50 | 2021-07-30 |
| 9 | Marker | 2 | 30 | 2021-08-13 |
| 10 | Scissors | 1 | 60 | 2021-08-13 |
The results show that all ten records are inserted successfully using a single query.
Leave a Reply