The programming languages such as PHP and C has a sleep(sec) function to pause the execution for a fixed amount of time. Java has a thread.sleep(), python has time.sleep(), and GO has time.sleep(2*time.second).
Unlike other languages, JavaScript doesn’t have any sleep() function. We can use some approaches for simulating the sleep() function in JavaScript. The features such as promises and async/await function in JavaScript helped us to use the sleep() function in an easier way.
The await is used to wait for a promise and can only be used in an async function. The behavior of JavaScript is asynchronous, so there is a concept of promises to handle such asynchronous behavior. Because of this asynchronous behavior, it continues its work and does not wait for anything during execution. Async/await functions help us to write the code in a synchronous manner.
How to use sleep function in JavaScript?
Before implementing the sleep function in JavaScript, it is important to understand the execution of the JavaScript code.
Syntax of sleep() in JavaScript
sleep(delayTime in milliseconds).then(() => {
// code to be executed
}) The sleep() function can be used along with the async/await to get the pause between the execution. The syntax for the same is given as follows:
Syntax
const func = async () => { await sleep(delayTime in milliseconds)
//code to be executed
}
fun() The above syntaxes are the way to implement sleep functionality in JavaScript. Now, we will see the examples of using the sleep() function in JavaScript.
Example1
In this example, we are using the sleep() function with the async/await functionalites. There is a function fun() is defined with some statements. Initially, the text “Hello World” is displayed on the screen once the function is started. Then, because of the sleep function the fun() is paused for 2 seconds. After the completion of the given time period, the text “Welcome to the javaTpoint.com” will be displyed on the screen and repeated until the termination of the loop. The text is going to be repeated 10 times on the screen with a pause of two seconds on every iteration of the loop.
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Example of using sleep() in JavaScript </h1>
<script>
function sleep(milliseconds) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, milliseconds));
}
async function fun() {
document.write('Hello World');
for (let i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
await sleep(2000);
document.write( i + " " + "Welcome to the javaTpoint.com" + " " + "</br>");
}
}
fun();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
After the execution of the above code, the output will be –
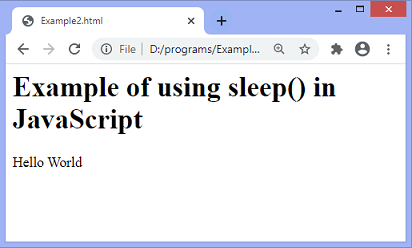
After two seconds, the output will change –
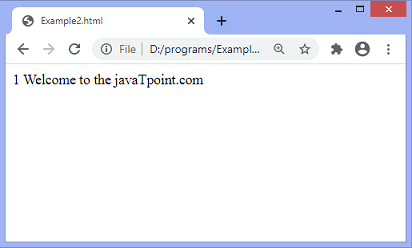
The loop will iterate 10 times with a pause of 2 seconds on every iteration.
Example2
Here, we are creating a promise with the setTimeout() function. The setTimeout() function executes code after the specified amount of time. We are also using the then() method, which executes the required function after the completion of the promise.
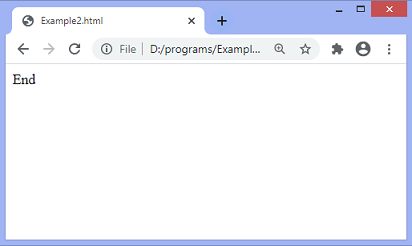
Initially, some of the statements are displayed on the screen. Then, after the delay of 2 seconds, the text “End” will be displayed on the screen.
This approach is preferred to delay a function. Because of using promises, it is supported in ES6.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Example of using the sleep() in JavaScript</h1>
<p>
There is a sleep of 2000 milliseconds
</p>
<script>
let sleep = ms => {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
};
document.write("Begin" + "<br>");
document.write("Welcome to the javaTpoint.com" + "<br>");
sleep(2000).then(() => {
document.write("End");
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
After the execution of the above code, the output will be –
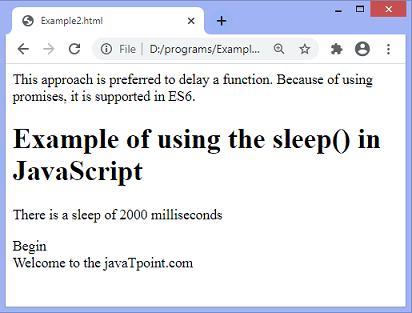
After the delay of 2 seconds, the output will be –
Leave a Reply