The parse() method in JavaScript is used to parse the specified date string and returns the number of milliseconds between the specified date and January 1, 1970. If the string does not have valid values or if it is not recognized, then the method returns NaN.
The counting of milliseconds between two specified dates helps us to find the number of hours, days, months, etc. by doing easy calculations.
Syntax
date.parse(datestring); It contains a single parameter string that represents a date. This method returns a number that represents the number of milliseconds.
Let’s see some illustrations of using the parse() method. In the first example, we are passing the valid date value, and in the second example, we are passing the invalid date value to see the result.
Example1
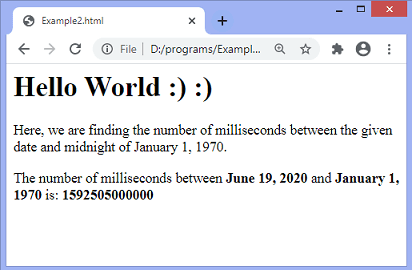
In this example, we are passing a valid date to get the number of milliseconds between the specified date and midnight of January 1, 1970.
Here, the specified date is “June 19, 2020”.
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Hello World :) :) </h1>
<p> Here, we are finding the number of milliseconds between the given date and midnight of January 1, 1970. </p>
<script>
var d1 = "June 19, 2020";
var m1 = Date.parse(d1);
document.write("The number of milliseconds between <b> " + d1 + "</b> and <b> January 1, 1970 </b> is: <b> " + m1 + "</b>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
Example2
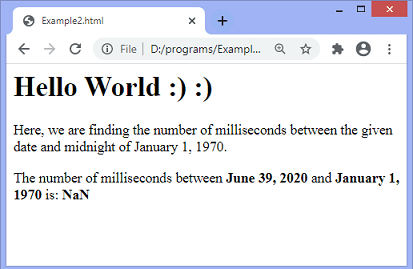
In this example, we are passing an invalid date to see what happens when we provide invalid input.
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Hello World :) :) </h1>
<p> Here, we are finding the number of milliseconds between the given date and midnight of January 1, 1970. </p>
<script>
var d1 = "June 39, 2020"; //an invalid date
var m1 = Date.parse(d1);
document.write("The number of milliseconds between <b> " + d1 + "</b> and <b> January 1, 1970 </b> is: <b> " + m1 + "</b>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
In the output, we can see the result is NaN.
Leave a Reply