The onresize event in JavaScript generally occurs when the window has been resized. To get the size of the window, we can use the JavaScript’s window.outerWidth and window.outerHeight events. We can also use the JavaScript’s properties such as innerWidth, innerHeight, clientWidth, ClientHeight, offsetWidth, offsetHeight to get the size of an element.
In HTML, we can use the onresize attribute and assign a JavaScript function to it. We can also use the JavaScript’s addEventListener() method and pass a resize event to it for greater flexibility.
Syntax
Now, we see the syntax of using the onresize event in HTML and in javascript (without addEventListener() method or by using the addEventListener() method).
In HTML
<element onresize = "fun()"> In JavaScript
object.onresize = function() { myScript }; In JavaScript by using the addEventListener() method
object.addEventListener("resize", myScript); Let’s see some of the illustrations to understand the onresize event.
Example
In this example, we are using the HTML onresize attribute. Here, we are using the window.outerWidth and window.outerHeight events of JavaScript to get the height and width of the window.
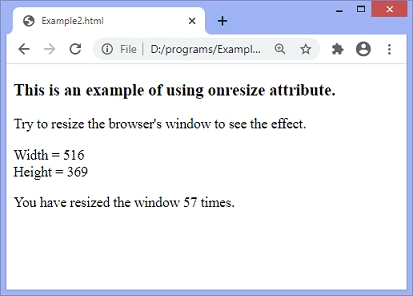
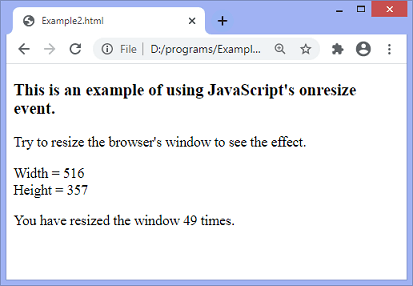
When the user resizes the window, the updated width and height of the window will be displayed on the screen. It will also display how many times the user tried to resize the window. When we change the height of the window, the updated height will change accordingly. Similarly, when we change the width of the window, the updated width will change accordingly.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
var i = 0;
function fun() {
var res = "Width = " + window.outerWidth + "<br>" + "Height = " + window.outerHeight;
document.getElementById("para").innerHTML = res;
var res1 = i += 1;
document.getElementById("s1").innerHTML = res1;
}
</script>
</head>
<body onresize = "fun()">
<h3> This is an example of using onresize attribute. </h3>
<p> Try to resize the browser's window to see the effect. </p>
<p id = "para"> </p>
<p> You have resized the window <span id = "s1"> 0 </span> times.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
After the execution of the above code, the output will be –
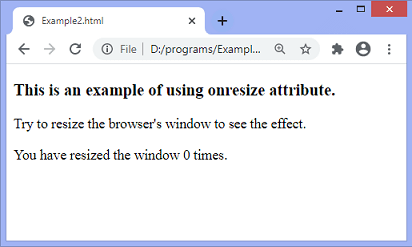
When we try to resize the window, the output will be –
Example – Using JavaScript
In this example, we are using JavaScript’s onresize event.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h3> This is an example of using JavaScript's onresize event. </h3>
<p> Try to resize the browser's window to see the effect. </p>
<p id = "para"> </p>
<p> You have resized the window <span id = "s1"> 0 </span> times.</p>
<script>
document.getElementsByTagName("BODY")[0].onresize = function() {fun()};
var i = 0;
function fun() {
var res = "Width = " + window.outerWidth + "<br>" + "Height = " + window.outerHeight;
document.getElementById("para").innerHTML = res;
var res1 = i += 1;
document.getElementById("s1").innerHTML = res1;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
After the execution of the above code, the output will be –
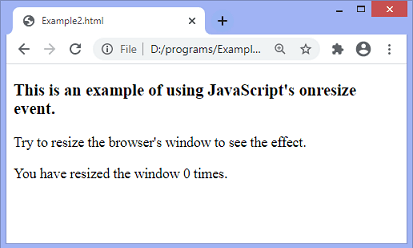
When we try to resize the window, the output will be –
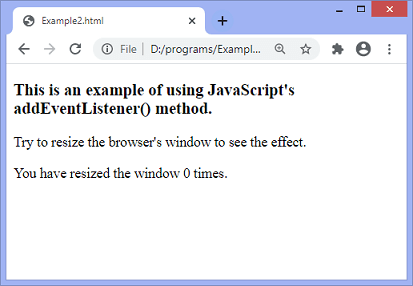
Example – Using addEventListener() method
In this example, we are using JavaScript’s addEventListener() method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h3> This is an example of using JavaScript's addEventListener() method. </h3>
<p> Try to resize the browser's window to see the effect. </p>
<p id = "para"> </p>
<p> You have resized the window <span id = "s1"> 0 </span> times.</p>
<script>
window.addEventListener("resize", fun);
var i = 0;
function fun() {
var res = "Width = " + window.outerWidth + "<br>" + "Height = " + window.outerHeight;
document.getElementById("para").innerHTML = res;
var res1 = i += 1;
document.getElementById("s1").innerHTML = res1;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
After the execution of the above code, the output will be –
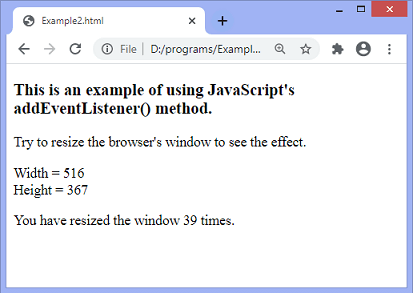
When we try to resize the window, the output will be –
Leave a Reply