The alert() method in JavaScript is used to display a virtual alert box. It is mostly used to give a warning message to the users. It displays an alert dialog box that consists of some specified message (which is optional) and an OK button. When the dialog box pops up, we have to click “OK” to proceed.
The alert dialog box takes the focus and forces the user to read the specified message. So, we should avoid overusing this method because it stops the user from accessing the other parts of the webpage until the box is closed.
We can understand the usefulness of the alert method using an example. Suppose we have to fill a form for an identity card. It asks about the date of birth for the eligibility criteria of the identity card. If the age is 18 years or above, then the process will continue. Otherwise, it will show a warning message that the age is below 18 years. This warning message is the ‘Alert Box’.
Another example is suppose a user is required to fill the form in which some mandatory fields are required to enter some text, but the user forgets to provide the input. As the part of the validation, we can use the alert dialog box to show a warning message related to fill the textfield.
Rather than showing the warnings or errors, the alert dialog box can be used for normal messages such as ‘welcome back’, ‘Hello XYZ’, etc.
Syntax
alert(message) Values
message: It is an optional string that specifies the text to display in the alert box. It consists of the information that we want to show to the users.
Let’s see some examples of the JavaScript alert() method.
Example1
In this example, there is a simple alert dialog box with a message and an OK button. Here, there is an HTML button which is used for displaying the alert box. We are using the onclick attribute and call the fun() function where the alert() is defined.
<html>
<head>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function fun() {
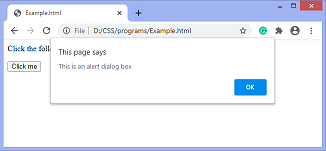
alert ("This is an alert dialog box");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p> Click the following button to see the effect </p>
<form>
<input type = "button" value = "Click me" onclick = "fun();" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output
After clicking the button, the output will be –
Example2
In this example, there is an alert dialog box with a message and an OK button. Here, we are using the line-breaks in the message of the alert box. The line breaks are defined by using the ‘\n’. The line breaks make the message readable and clear. We have to click the given button to see the effect.
<html>
<head>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function fun() {
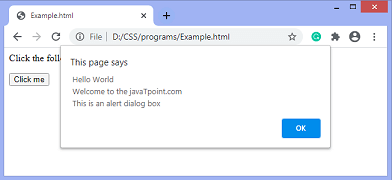
alert (" Hello World \n Welcome to the javaTpoint.com \n This is an alert dialog box ");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p> Click the following button to see the effect </p>
<form>
<input type = "button" value = "Click me" onclick = "fun();" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output
After clicking the button, the output will be –
Example
In this example, there is an alert dialog box with a message and an OK button. Here, the alert box displays the URL of the corresponding page. The URL is defined by using the alert(location.hostname); statement.
<html>
<head>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function fun() {
alert(location.hostname);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p> Click the following button to see the effect </p>
<form>
<input type = "button" value = "Click me" onclick = "fun();" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Leave a Reply