HTML <source> tag is used as a child element to define more than one media resources for <audio>, <video>, and <picture> element.
It is used to provide the same media content with different formats such as mp3, mp4, etc.
When we embed multiple resources with the same content but different format then the browser may choose the most compatible format and display or play that media file.
The <source> tag was introduced in HTML5.
Syntax
<source src=" " type=" "> Following are some specifications about the HTML <source> tag
| Display | Inline |
| Start tag/End tag | Empty tag( Only start tag) |
| Usage | Media resource |
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML source tag</title>
</head>
<body>
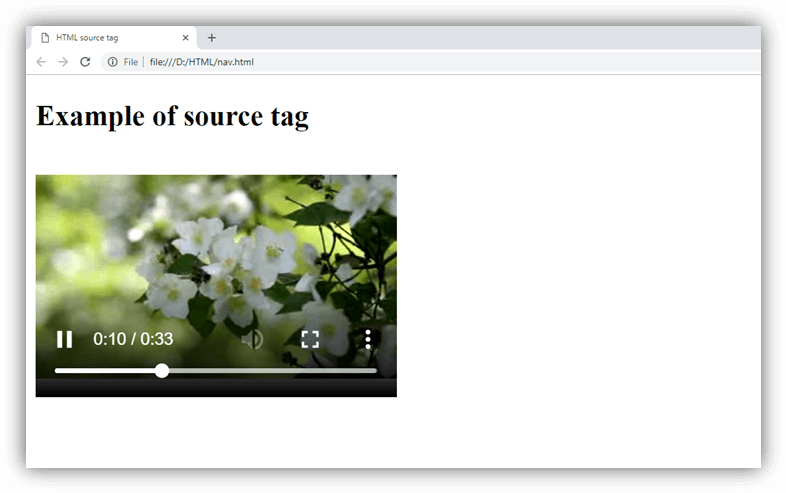
<h2>Example of source tag</h2>
<video controls="controls" height="200" width="300">
<source src="flower.webm" type="video/webm" >
<source src="flower.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the HTML5 video element.
</video>
</body>
</html>Output:
Attribute:
Tag-specific attributes:
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| media | Media_query | It determines that for which media/device the linked source is optimized. |
| sizes | It specifies acceptable image sizes for different page layout. | |
| src | It determines the URL of media files. | |
| srcset | Specifies the URL of the image for different situations. It is only used when <source> is child of <picture> element. | |
| type | video/ogg video/mp4 video/webm audio/ogg audio/mpeg | It determines the media type of resource. |
Global attribute:
The <source> tag supports the Global attributes in HTML.
Event attribute:
The <source> tag supports the Event attributes in HTML.
Supporting Browsers
| Element |  Chrome Chrome |  IE IE |  Firefox Firefox |  Opera Opera |  Safari Safari |
| <source> | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Leave a Reply